Australia is no stranger to earthquakes, yet our planning polices have not adapted
- Written by Mark Maund, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, School of Architecture and Built Environment, University of Newcastle
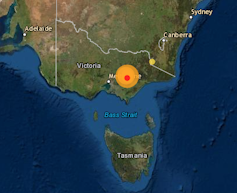
Southeastern Australia was yesterday rocked by a magnitude-5.8 earthquake[1] with its epicentre near Mansfield in Victoria’s northeast.
The quake, which was followed by two smaller tremors, was powerful enough to damage buildings 130 kilometres away in Melbourne, and the shaking was felt as far away as Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide and Launceston[2].
One Victorian acquaintance said they felt the ground shake so much that “I could see things outside shaking and was wondering if I should dive under the desk”, while Melburnians told[3] of the terrifying swaying of apartment blocks. The damage to buildings confirmed the impact a large quake can have on our built environment.
The earthquake even prompted building evacuations in Newcastle, NSW[4], the scene of Australia’s most damaging earthquake on record in 1989. That quake, which had a magnitude of 5.6 and an epicentre roughly 15km southwest of the Newcastle CBD, killed 13 people and hospitalised 160[5], and left 1,000 people homeless.
Yet in the three decades since, many large buildings have been constructed in the Newcastle CBD, including a 22-storey residential tower[6]. The result is that many more people now live near the site of Australia’s deadliest-ever earthquake.
This does not mean we should immediately abandon these popular areas. But we do need a consistent planning approach, to decide where we build and what level of risk we should accept. Natural hazards should be a central focus of planning, and communities should be told explicitly about the risks of living in a particular area.
Earthquakes are far from unknown[7] in Australia. Yet our planning system does not explicitly consider which areas are at unacceptable risk from earthquakes. We continue to build in earthquake-prone areas across Australia, relying solely on building design to manage these risks.
This isn’t good enough. We urgently need a national planning policy that takes account of earthquake risk, to strengthen and support building standards. Building standards alone are not sufficient. We also need to consider the number of people in an area, their ability to relocate during a disaster, and their access to emergency accommodation and recovery support.
Broader planning issues such as secondary roads for evacuation and long-term evacuation centres for those displaced must form part of the design of our cities and towns.
What do the current standards say?
Australia’s national construction code ranks buildings primarily from 1 (minor structures that are unlikely to endanger human life if they fail) to 4 (such as buildings or structures that are essential to post-disaster recovery including medical and emergency services and emergency shelters), based on relevant building standards[8] for earthquake risk[9]. A higher category indicates more stringent construction requirements for all buildings in that category to withstand an earthquake.
The standards also provide a “hazard design factor” that indicates requirements for buildings to withstand an earthquake in different parts of Australia. These design factors consider places such as Meckering and Dowerin in Western Australia to be highly hazardous with regard to earthquakes, whereas places like Newcastle are designated as lower-risk, despite having experienced an earthquake. Shepparton in Victoria, which is near the epicentre of yesterday’s earthquake, has an even lower rating.
While these construction standards provide some useful guidance to architects and planners, they arguably miss a key point. Earthquakes, generally speaking, are very rare but potentially very damaging. So we need to adapt our planning strategies to take account of this, rather than just relying on building standards.
Read more: We may never be able to predict earthquakes – but we can already know enough to be prepared[10]
We need a national planning policy
Australia doesn’t have a national planning agency, although such an agency would be vital to provide a consistent approach to planning issues such as natural hazards. At the very least, we urgently need a national planning policy that addresses the risk of natural hazards such as earthquakes. This policy needs to consider the legacy of historical planning decisions, and avoid future development in high-risk areas.
Similar to areas affected by floods or bushfires, we must think before we rebuild, and consider whether to rebuild in the same area at all. With specific regard to earthquakes, we need to consider whether a particular location allows us to construct buildings that will be safe, provide safe access and escape via road and public transport, and allow for adequate evacuation centres.
In earthquake-prone locations, we should consider the risk before approving tall buildings, those with large numbers of occupants, or those that cater for lots of people who are likely to need extra assistance in an emergency, such as hospitals, childcare and aged-care centres.
Read more: Earthquakes don’t kill people; buildings do. And those lovely decorative bits are the first to fall[11]
With Australia’s population set to exceed 49 million by 2066[12], bringing ever-taller buildings and more urban sprawl, earthquakes may have a growing impact on our lives. We need a strong, consistent and nationwide approach to considering natural hazards in planning as part of meeting our housing, employment and environmental needs.
Without this, we will continue to rely heavily on building standards, continue to develop in hazard-prone areas, and continue to experience damaging disasters. A national policy, in contrast, will help us build communities that are more resilient and safer.
References
- ^ rocked by a magnitude-5.8 earthquake (theconversation.com)
- ^ Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide and Launceston (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ told (www.news.com.au)
- ^ prompted building evacuations in Newcastle, NSW (www.newcastleherald.com.au)
- ^ killed 13 people and hospitalised 160 (www.ga.gov.au)
- ^ 22-storey residential tower (www.newcastleherald.com.au)
- ^ far from unknown (theconversation.com)
- ^ building standards (infostore.saiglobal.com)
- ^ earthquake risk (www.saiglobal.com)
- ^ We may never be able to predict earthquakes – but we can already know enough to be prepared (theconversation.com)
- ^ Earthquakes don’t kill people; buildings do. And those lovely decorative bits are the first to fall (theconversation.com)
- ^ exceed 49 million by 2066 (www.abs.gov.au)

















