From floods to fire? A climate scientist on the chances El Niño will hit Australia this year
- Written by Andrew King, Senior Lecturer in Climate Science, The University of Melbourne
After three soggy years of La Niña in a row, Australia has endured record-breaking floods, the latest of which has inundated the Kimberley[1] in Western Australia and across north and central Queensland[2].
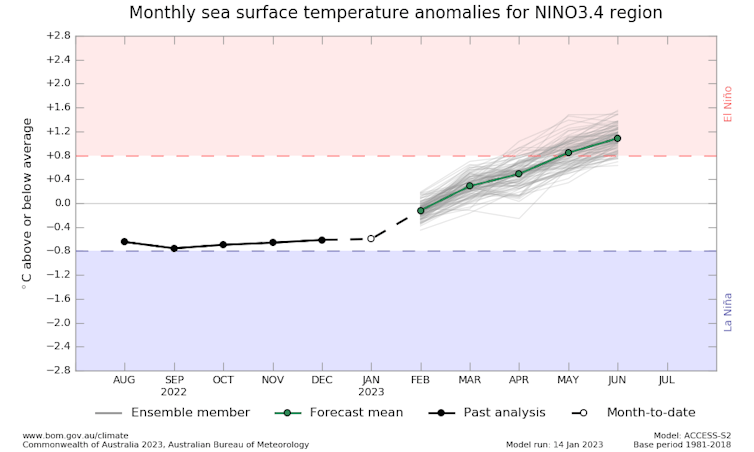
While the rains may have initially been a relief after the heat, drought and fires that came before, they have long outstayed their welcome. Thankfully, the latest update[3] from the Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) points to a continuing weakening of La Niña – but it also points to the possibility of El Niño emerging by the autumn.
You can think of El Niño as being like the opposite of La Niña. While La Niña is known for bringing cooler, rainy weather, El Niño brings hot, dry conditions. This means it’s often associated with drought, heatwaves and bushfires. The world’s hottest year on record in 2016 was an El Niño year.
Let’s take a closer look at BOM’s forecast and what Australians can expect in the coming months.
Read more: Disastrous floods in WA – why were we not prepared?[4]
The difference between El Niño, La Niña and climate change
La Niña and El Niño events are “climate drivers”, which means they are part of the natural oscillations of the Earth’s climate. Human-caused climate change, on the other hand, acts over a longer term, steadily bringing up the planet’s average temperature and exacerbating some of the impacts of La Niña and El Niño events.
La Niña is characterised by cooler waters than normal in the tropical eastern Pacific near Peru and Ecuador and warmer waters in the west Pacific including around northern Australia.
When we have La Niña we have an increased chance of wet conditions over northern and eastern Australia, especially in spring. The past three years with consecutive La Niña events have followed this pattern.
In contrast, El Niño is associated with warmer waters over the central and eastern Pacific Ocean and cooler waters in the west. El Niño conditions bring an increased chance of warmer and drier conditions in Australia.
For now we have a dissipating La Niña, and there is strong confidence it will continue to weaken over the coming weeks. We expect it to be properly finished by the end of summer.
The likelihood of El Niño forming
As we look further ahead, our confidence in what will happen next reduces. BOM’s outlook suggests El Niño conditions could arrive by late autumn, but other forecast models[5] point to a lower chance of El Niño emerging at all.
Forecasts of El Niño are challenging several months in advance, but particularly at this time of year when they have to overcome the “autumn predictability barrier[6]”. In autumn, there is less variation in the Pacific Ocean’s temperature and it’s harder to forecast if an El Niño or La Niña will emerge by winter.
We are by no means guaranteed a switch to El Niño, but there is a higher probability of an El Niño forming in the next few months than we’ve seen for several years.
Australia is also affected by other natural climate drivers, such as the Indian Ocean Dipole[7], which has a strong effect on winter weather. This climate driver is brought about by interactions between ocean currents and the atmosphere, and influences rainfall patterns around the Indian Ocean, including Australia.
Understanding the Indian Ocean Dipole.It’s currently forecast to move into a “positive phase” by early winter, which would favour a drier winter over most of Australia as well but this is also still uncertain[8].
From floods to drought?
With indications of a shift to El Niño and positive Indian Ocean Dipole, should we expect to swing from floods to drought?
Drought occurs on different timescales[9], but Australia’s most devastating droughts, which result in major agricultural losses and water restrictions, require several years of dry conditions.
With our dams full, it’s unlikely we’ll see a major drought form for a while. If we have an extended period without La Niña or negative Indian Ocean Dipole conditions, then drought may start to appear again[10]. However, the drier weather would also raise the risks of other hazards such as heatwaves and bushfires.
The horror 2019-2020 fire season[11] came off the back of a weak El Niño and a strongly positive Indian Ocean Dipole. Indeed, Australia’s hottest summer on record[12] was during the El Niño of 2018-2019.
This time, our three consecutive La Niña events have resulted in more vegetation growth. This means next summer, there will be more fuel for fires to burn.
Read more: Why drought-busting rain depends on the tropical oceans[13]
New heights for global temperatures
El Niño doesn’t just affect Australia. For example, during El Niño events we typically see a weaker Indian monsoon and drier conditions over southern Africa. East Africa, which has suffered greatly from drought[14] in recent times, is usually wetter during El Niño.
As El Niño events involve the warming of a large area of the Pacific Ocean they tend to raise the global average surface temperature by about one-tenth of a degree. While that might not sound like very much, it could push the global average surface temperature to record-breaking highs, particularly in the year after an El Niño forms.
Given the planet is rapidly warming due to our continuing high greenhouse gas emissions, and the fact we haven’t had a big El Niño for a while, even a moderate El Niño could mean the world experiences a new record hot year.
There is even the possibility the global average temperature could surpass 1.5℃[15] above pre-industrial levels for the first time.
While we’re aiming to keep global warming under 1.5℃ to meet the Paris Agreement, an individual year above this mark does not mean we have failed. Still, it’s not a good sign if we start to hit that mark.
Read more: Famine should not exist in 2022, yet Somalia faces its worst yet. Wealthy countries, pay your dues[16]
Is climate change altering El Niño?
It’s not yet clear exactly how climate change may be altering El Niño. However, there are indications climate change may be moving El Niño events towards the central Pacific[17] nearer the international dateline.
Climate change could also possibly strengthen rainfall responses to El Niño and La Niña over the Pacific[18] and elsewhere[19]. This may worsen both our floods and droughts in Australia, but more research is needed.
Unfortunately, in terms of global temperatures and Australian heatwaves, it’s clear the combination of human-caused climate change and a major El Niño event increases the likelihood of record-breaking events. An El Niño may not be a welcome a reprieve from the past few soggy years.
Read more: El Niño has rapidly become stronger and stranger, according to coral records[20]
References
- ^ the Kimberley (theconversation.com)
- ^ north and central Queensland (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ latest update (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ Disastrous floods in WA – why were we not prepared? (theconversation.com)
- ^ forecast models (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ autumn predictability barrier (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ Indian Ocean Dipole (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ but this is also still uncertain (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ Drought occurs on different timescales (theconversation.com)
- ^ start to appear again (theconversation.com)
- ^ horror 2019-2020 fire season (www.nature.com)
- ^ hottest summer on record (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ Why drought-busting rain depends on the tropical oceans (theconversation.com)
- ^ from drought (theconversation.com)
- ^ could surpass 1.5℃ (www.newscientist.com)
- ^ Famine should not exist in 2022, yet Somalia faces its worst yet. Wealthy countries, pay your dues (theconversation.com)
- ^ towards the central Pacific (theconversation.com)
- ^ Pacific (www.nature.com)
- ^ elsewhere (agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ El Niño has rapidly become stronger and stranger, according to coral records (theconversation.com)

















