how does music get onto a cassette tape?
- Written by Christopher Wenn, Tutor in Production (Technical), The University of Melbourne
How does music get onto a cassette tape? — Paul, age 9, Adelaide
Hi Paul!
That’s a great question. To answer it very briefly, music is recorded onto a cassette tape using electricity and a magnetic field. Now let me explain what I mean by that.
Sound gets turned into electricity
Imagine you’re singing into a microphone while playing a guitar. When you sing, you use your vocal cords in your throat, your mouth and your breath to make the air around you vibrate — and these vibrations are what create sound.
Similarly, when you pluck or strum the strings of a guitar, this causes the wooden body of the instrument to vibrate, which also vibrates the air inside the guitar, creating sound.
Both the microphone and the guitar “pickup” (a special kind of microphone for “picking up” sound from an instrument) have tiny magnets that vibrate with the movements of air, and produce an electrical current.
The current flows through the microphone and guitar cables to the tape recorder, through which a plastic tape is slowly moving. The electrical signal creates a magnetic field in the recording head and this is what allows sound to be recorded.
But what happens within the tape recorder itself during this process?
How magnetic tape works
A cassette tape is a plastic shell that surrounds two rotating spools.
 A collection of cassette tapes/
Mike Flamenco/unsplash
A collection of cassette tapes/
Mike Flamenco/unsplash
Another long, thin piece of plastic is wound around the spools. This is the “magnetic tape” on which the sound is recorded.
This tape is covered with a magnetic material that contains iron, and which reacts when it comes close to a magnetic field. The material could be iron oxide, chromium dioxide, or sometimes barium ferrite.
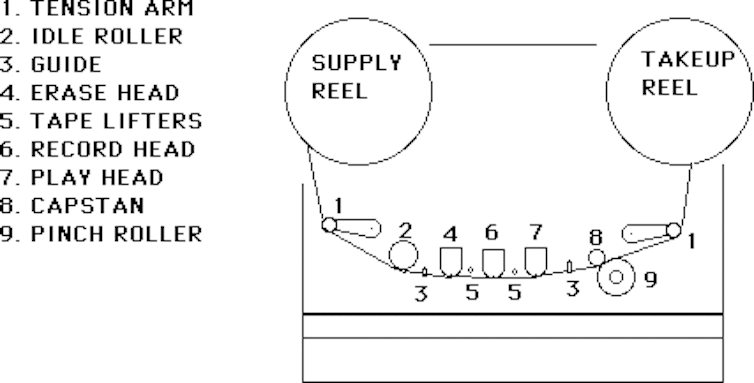 A diagram of a magnetic tape recorder showing the mechanical parts.
University of California Santa Cruz Electronic Music Studio
A diagram of a magnetic tape recorder showing the mechanical parts.
University of California Santa Cruz Electronic Music Studio
In the diagram above, we can see the basic parts of a tape recorder. Here’s what happens when an empty cassette tape is used to record sound.
The magnetic tape starts on the supply reel and a motor on the takeup reel winds the tape past the heads (4, 6, 7). Each head contains metal coils. When electricity is sent to the coils in the record head (6), it generates a tiny magnetic field.
When the tape enters the magnetic field generated by the record head, the magnetic particles on it align in proportion to the strength of the field. The loudness and pitch of the sound (how high or low it is) make the magnetic particles align in different patterns as the tape passes through.
Later, if we want to play our recording back, we wind the tape past the play head (7), where the pattern of the magnetic particles recorded on the tape produces an electrical signal that is converted back to sound.
These particles will stay in the same arrangement unless they are exposed to a new magnetic field — so a tape can be played back many times, until it wears out!
The remaining head is the erase head (4). This lets us erase sound from a tape by using a constant electrical charge to “reset” the magnetic material on the tape as it passes through, erasing any previous recordings.
The capstan, rollers and arms all help to keep the tape stretched out as it passes through the heads, so that it moves at the same speed and gets a good-quality recording.
A little history
Cassette tapes were developed by the company Philips in 1963[1].
 An image of the first model of compact cassette tape sold by Philips in the 1960s.
Philips USA
An image of the first model of compact cassette tape sold by Philips in the 1960s.
Philips USA
Although recording to tape had been possible since the 1930s[2], the technology was large, awkward and expensive. The Philips Compact Cassette was cheap, portable (small enough to carry around) and could be used at home or in the office, with basic recording equipment.
But when Masaru Ibuka, the co-founder of the Japanese company Sony, wanted a way to listen to his favourite music on long flights, he sparked an invention that would change the[3] way we listened to music forever: the Sony Walkman.
 The Original Sony Walkman TPS L.
Binarysequence/wikimedia
The Original Sony Walkman TPS L.
Binarysequence/wikimedia
The Walkman was released in 1979 and brought music into every part of our lives. Not just our homes, or cars — but anywhere at any time! It is more or less a portable cassette player that connects with headphones.
Since then we have seen huge improvements in portable music technology, with MP3 players coming out in 1997 and eventually the Apple iPod’s release in 2001[4].
Today, we don’t even need a special device just to record or play music. We can do everything on our phones! But cassette tapes were the first invention that let people easily record and play on the go.
Read more: How do astronauts go to the bathroom in space?[5]
References
- ^ developed by the company Philips in 1963 (www.usa.philips.com)
- ^ had been possible since the 1930s (www.vox.com)
- ^ that would change the (www.sony.com.au)
- ^ release in 2001 (www.cnet.com)
- ^ How do astronauts go to the bathroom in space? (theconversation.com)
Read more https://theconversation.com/curious-kids-how-does-music-get-onto-a-cassette-tape-165759


















