41% of full-time and 35% of part-time jobs can be done from home
- Written by Mehmet Ulubasoglu, Professor of Economics, Head of the Department of Economics and Director of the Centre for Energy, the Environment and Natural Disasters, Deakin University
Victoria’s outbreak of COVID-19 infections, with 75 more cases identified overnight[1] on top of 173 cases the previous five days, underlines the need to stick with social distancing measures wherever possible.
Working at home, in particular.
About 23 cases have been linked[2] to Melbourne’s Stamford Plaza hotel, where people flying in from overseas have been quarantined. Victorian premier Daniel Andrews said on Sunday the hotel outbreak might be due to staff sharing a cigarette lighter or carpooling to work.
Read more: Victoria's coronavirus hotspots: not quite a second wave, but still cause for concern[3]
So what proportion of the workforce in Australia can feasibly work from home?
We estimate 39% of all jobs in Australia – 41% full-time and and almost 35% of part-time – can be done from home. Full-time jobs are more teleworkable than part-time jobs. Women are also more likely to have teleworkable jobs – 46% to 33% of men.
How we made our calculations
To make these estimates, we used the methodology of University of Chicago economists Jonathan Dingel and Brent Neiman. In June[4] they published findings that 37% of jobs in the United States could be done at home.
They took data from the Occupational Information Network[5], a US government-funded online database describing about 1,000 occupations in the US. Any job involving outdoor work, operating vehicles or equipment, general physical activities, handling objects, dealing directly with the public and so on was deemed not teleworkable.
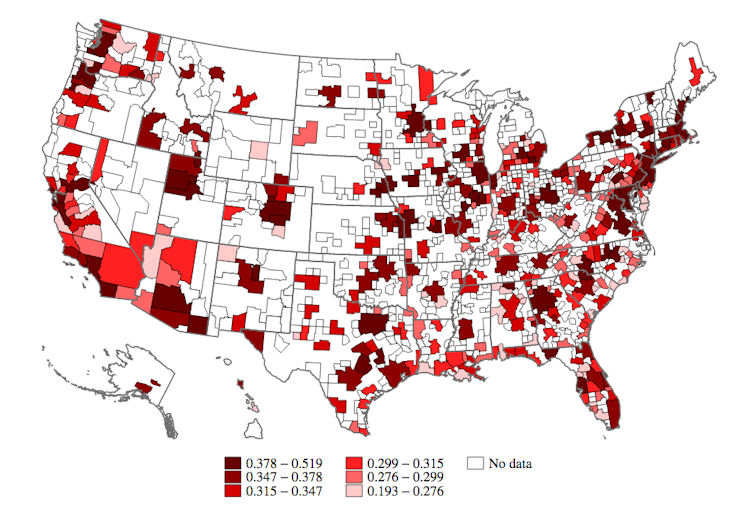 This map shows the share of jobs that can be done at home for 388 US statistical areas.
Jonathan Dingel & Brent Neiman, CC BY-ND[6][7]
This map shows the share of jobs that can be done at home for 388 US statistical areas.
Jonathan Dingel & Brent Neiman, CC BY-ND[6][7]
Dingel and Nieman also made calculations for 85 other countries. In general, they concluded, the higher per capita GDP, the greater the teleworkability. Sweden and Britain, for example, exceeded 40% while Mexico and Turkey were less than 25%.
Read more: Heading back to the office? Here's how to protect yourself and your colleagues from coronavirus[8]
Australian assumptions
To apply Dingel and Nieman’s approach to Australia we assumed the nature of work and general economic activity is similar to the US.
Next we converted occupational classifications from the Australasian equivalent of the US database – the Australian and New Zealand Standard Classification of Occupations[9] (ANZSCO) compiled by the Australian Bureau of Statistics and Stats NZ[10].
The ANZSCO classifications do not exactly match the International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO) used by the US database. In such cases we evenly distributed the jobs in the Australian classification between the corresponding international classifications.
Our estimate is therefore a proximate indicator of teleworkability. Our results broadly confirm those by Harvard University economist James Stratton[11] (an Australian) using Dingel and Niemans’s methodology.
Stratton’s results highlighted the geographic and socio-economic disparities in teleworkability: for example, 45% of jobs in Australia’s eight major cities can be done at home, compared to 33% elsewhere.
To complement this work, we’ve drilled into the gender differences.
Teleworking favours women
Importantly, we estimate 45.7% women have teleworkable jobs compared to 32.9% of men.
This is due to about 60% of female employment being concentrated in administrative, clerical, teaching and customer-service jobs.
Teleworkability is highest in the Australian Capital Territory (50.3%), followed by Victoria (40%), the Northern Terrioty (39.5%), Queensland (37.2%), WA (36.8$), SA (36.2%) and Tasmania (34.9%).
Full-time jobs are more teleworkable than part-time jobs, 41% to 34.7%. Moreover, 51.7% of women with full-time jobs can work from home, compared with 34.7% of men.
Younger employees are less likely to have teleworkable jobs, particularly in part-time employment. Young men in part-time jobs are the least likely to have a job they can do at home.
The labour-market effects of working from home remain to be better understood. But these calculations – as broad as they are – provide some good news on the economic gender impacts of COVID-19[12], hitting women marginally more.
While working from home is not for everyone, these estimates show it’s a viable arrangement for many.
And a crucial measure for Australia to beat the coronavirus pandemic.
References
- ^ 75 more cases identified overnight (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ 23 cases have been linked (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ Victoria's coronavirus hotspots: not quite a second wave, but still cause for concern (theconversation.com)
- ^ June (bfi.uchicago.edu)
- ^ Occupational Information Network (www.onetonline.org)
- ^ Jonathan Dingel & Brent Neiman (bfi.uchicago.edu)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Heading back to the office? Here's how to protect yourself and your colleagues from coronavirus (theconversation.com)
- ^ Australian and New Zealand Standard Classification of Occupations (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ Stats NZ (www.stats.govt.nz)
- ^ Harvard University economist James Stratton (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ gender impacts of COVID-19 (theconversation.com)
Authors: Mehmet Ulubasoglu, Professor of Economics, Head of the Department of Economics and Director of the Centre for Energy, the Environment and Natural Disasters, Deakin University