Once safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines are available, tough choices will need to be made about who gets the first shots.
A committee of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine – at the behest of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health – has proposed an equitable way to allocate the vaccine.
They recommend first responders and health care workers take top priority. Older adults in congregate living situations would also be part of a first vaccination phase, according to the plan.
We are faculty at Johns Hopkins University and the University of Southern California who have spent decades studying health economics and epidemiology. One of us is a member of the National Academy of Medicine.
Having seen firsthand the real risks of rapid, asymptomatic spread of COVID-19 among younger adults, we disagree with some of the recommendations. Asymptomatic spread is shutting down schools and universities nationwide and threatening surrounding communities.
We argue that this pandemic requires a different model for making vaccination choices. After taking care of essential workers, vaccinations should be given to the biggest transmitters of the virus – mostly the young – and only then to the most vulnerable.
Lessons from 2009 flu epidemic
The textbook vaccine model goes out the window when novel viruses emerge.
Some lessons can be drawn from the 2009 H1N1 flu epidemic, which killed an estimated 500,000 people around the world. In the U.S, President Barack Obama declared the spread a national emergency.
A vaccine was developed as early as the fall of 2009. However, only 16 million doses were initially available. The CDC was required to make some difficult decisions about allocation. Some states requested 10 times the amount they were allocated.
In the end, the CDC allocated the vaccine strictly in proportion to a state’s population – that is, on a per capita basis. States then allocated them, often with priority to infants and the elderly, along with people at high risk.
This priority – to protect the most frail – has been public policy since at least the 1957-1958 influenza pandemic.
Later studies, however, have shown that a better way to protect older people was to control spread among the young, which often has meant vaccinating school-age children early.
One of the lessons from these past pandemics is that vaccinating the likely asymptomatic spreaders early can avert multiple infections with others.
[You need to understand the coronavirus pandemic, and we can help. Read The Conversation’s newsletter.]
The superspreaders
The experience of the past few months has shown how important it is to check transmission with COVID-19. A recent study found that as few as 10% of those infected lead to 80% of the infection cases. What has made it more difficult is that up to 40% of those who carry the virus, often known as superspreaders, show no symptoms at all.
Very few of the COVID-19 superspreaders are elderly. It is the younger people who have a much greater propensity to resume social lives at schools and in other venues.
Among the young are a subset of highly social people with wide circles of friends who become the most fertile ground for the spread of COVID-19. These young people also have a much lower risk of death or even severe symptoms, which also means they are more likely to infect others.
Cases have been spiking in the 15- to 25-year-old age group, another likely sign that they are propelling the spread of the virus. A recent outbreak on the University of Southern California’s fraternity row infected at least 40 people.
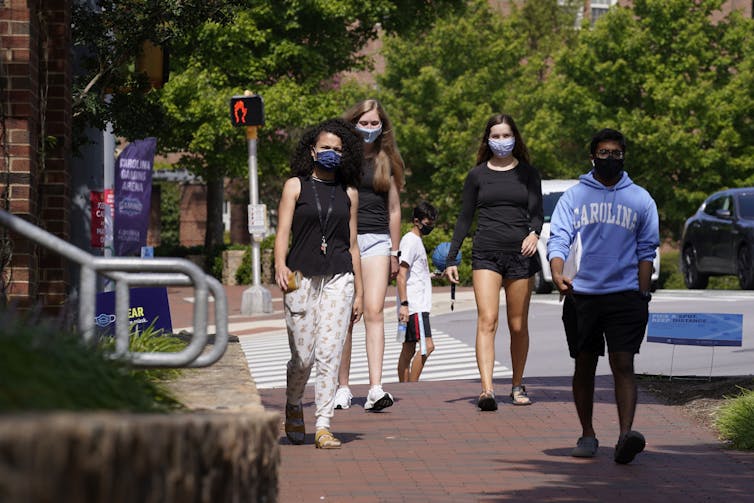

The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association reports that at least 338,000 children have tested positive for the virus through July 30, with more than a quarter of that number having tested positive in just the last two weeks of that month.
More broadly, younger residents in the virus hot spot of Los Angeles County make up the majority of positive new cases. In California, young people between 18 to 34 years of age account for more than one-third of cases.
Young versus old
Anticipating that young people will engage in activities that spread the virus, many universities put their fall classes exclusively online. Some that decided to go in-person had to close after as little as a week on campus.
With or without a vaccine, the best strategy for older Americans, especially those with underlying medical conditions, is avoiding contact with potential carriers.
Optimally, older people will drive down deaths by staying home in large numbers, and younger people will drive down infections by getting vaccinated in even larger numbers. It all works if the vaccine is effective and enough people take it.
We predict the pressures and politics around prioritizing vaccine distribution will be intense. We argue that they key will be to take the most beneficial route, not the most obvious one. With a full-scale public health campaign behind it, that will mean prioritizing those who are driving transmission, not those who are most vulnerable.
As counterintuitive as such a strategy may appear, plenty of evidence shows this would be the right approach.