Chemical Bunds and its needs
- Written by The Times
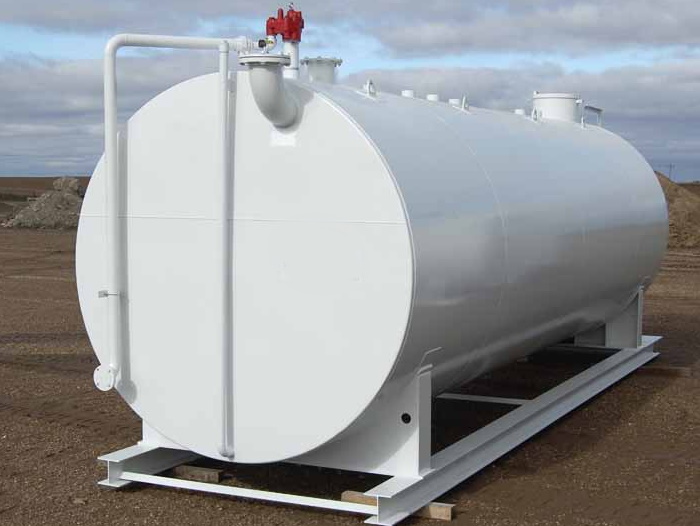

If you have a business that involves water and wastewater treatment, banding could be an essential element to prevent leaking store chemicals and protecting the environment. The guidance you would get on bunding chemical manufacturing or in petrochemical sectors might differ from that of other industries. If you look up the term bund, you would be able to come up with advice that is relevant to those industries or even to the confinement of large water bodies. Hence, you should avoid confusion.
If you are looking to install a Portable bund in Australia, you could easily find it online, order it and get it installed from various companies.
Why do we need chemical bunds?
A chemical bund is a structure that surrounds an area that contains hazardous liquids or chemicals which provides a secondary containment in case of a leak or a spill.
The structures could be permanently built for handling smaller volumes or could be portable if you have to shift the chemical storage area somewhere else. Bunds prevent the spread of leaking liquids and provide time to the operators to find a remedy for the leak and its cause.
They act as barriers under and around the storage tanks, IBCs (Intermediate Bulk Containers) and stored drums. When it comes to freestanding storage tanks, a permanent bundle could be designed into a plant's layout by considering the future inspection, cleaning and maintenance needs.
Chemical dosing plants supplied as packaged solutions often have integrated bund that could form the base structure and support a kiosk-type cover. Temporary bunds are available in a variety of sizes and designs. It includes IBC bunds that are constructed for movement by forklift trucks and are often known as "pallet bunds".
Pallet bunds protect against spillage from IBCs or drums while transporting and continue to provide bunding where the containers are stored. IBCs are delivery containers and are not designed for use as permanent storage tanks. They often serve storage purposes in the short or medium term. However briefly it is stored, IBC container chemicals should never be left un-bunded. Temporary IBC bunds could be inexpensive and easily available so that you could install them and not take any risk. However, you could also click on the "Buy now" button in an ad if you come across portable bund ads online that match your requirements.
A sudden burst in a chemical container would be dangerous when it comes to localised damage and effects on personnel as well as the environment. In most cases, the leakage could be more gradual and the impact might take longer to appear. Either way, if there is no bund to contain it, the chemical would reach a river, stream or any other natural habitat and might cause devastation.
Companies that allow such pollution should be held responsible for the after-effects like environmental destruction, fishkill and other hazards to the human population. This would lead to the expense of enforcement undertakings, fines, remedial works and other costs.
You look up online, you could find prosecution against various companies who are found to be responsible for unforeseen chemical leaks with penalties and huge fines. Properly installed, well-designed and carefully maintained buildings could avoid all such consequences.