Cheap shots aside, Chalmers has work to do to improve his new 'wellbeing' framework
- Written by John Hawkins, Senior Lecturer, Canberra School of Politics, Economics and Society, University of Canberra
The Albanese government’s new “Measuring What Matters[1]” framework for a wellbeing economy has been criticised for relying on out-of-date data in several crucial measures. But that’s an easy and somewhat cheap criticism to make.
Notably, the Treasury document reports “little change” in overall life satisfaction based on statistics from 2020[2], and “stable” psychological distress, based on statistics from 2018[3].
As The Australian newspaper has editorialised[4], this old data “fails to reflect the COVID-19 pandemic, billions of dollars in extra NDIS spending, and the most aggressive series of interest rate hikes in a generation”.
True, but given these are the most recent years on which the Australian Bureau of Statistics has published data, that’s a relatively cheap shot. It’s as if the newspaper wants to find fault with the document, labelling it “a pitch to progressives” and a “fad”.
The document is more than that. It should be acknowledged as a significant and positive step in the right direction by Australia’s Treasury, in keeping with international best practice.
At the same time, it should be recognised that the measures being used need improvement, both in terms of regularity and how much they capture differences masked by national averages
Read more: Chalmers 'measures what matters' – tracking our national wellbeing in 50 indicators[5]
We’re late to this party
When the then shadow Treasurer Jim Chalmers outlined his plan for a wellbeing budget in 2020, his opposite number Josh Frydenberg[6] mocked it as a “yoga mat and beads[7]” approach to economic management.
But the need to shift away from using the blunt instruments of national income or gross domestic product (GDP) to measure progress has long been recognised. Even the inventor of GDP, Simon Kuznets, said a nation’s welfare[8] can “scarcely be inferred from a measurement of national income”.
New Zealand, Wales, the United Kingdom, India and Canada are all ahead[9] of Australia in adopting wellbeing frameworks to shape their budget decisions. International institutions such as the OECD[10] and United Nations are working along similar lines.
The new statement is in some ways a restoration of the Treasury’s wellbeing framework[11] developed in the early 2000s under the Howard government, championed by department head Ken Henry and inspired by the work of Nobel prizewinner Amartya Sen[12]. It was quietly dropped in 2016[13] under the Turnbull government.
The problem with ‘average’ Australians
There are various approaches to measuring wellbeing[14]. One way is to amend GDP by taking out “bad things” (pollution, loss of biodiversity, smoking) and include “good things” not currently included (such as unpaid caring work done in the home).
The approach of Measuring What Matters is to use a “dashboard” of 50 indicators of inclusion, fairness and equity over five areas: health, security, sustainability, cohesion and prosperity. The measures for health, for example, include life expectancy, mental health, prevalence of chronic conditions, and access to health and support services.
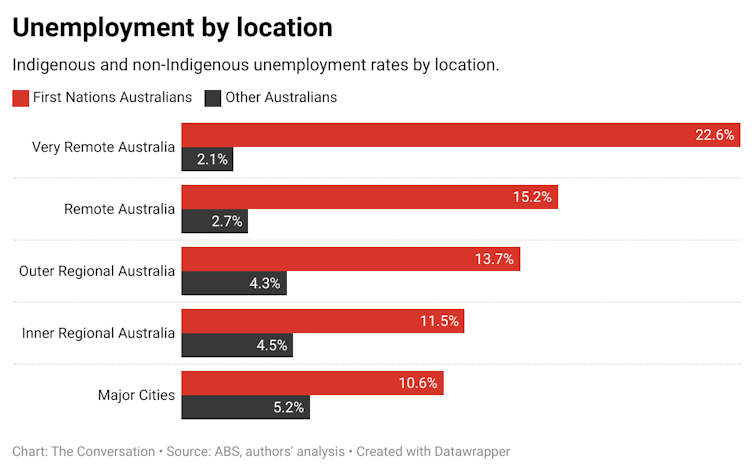
For these measures to be meaningful and useful to the budget process, they need to be both timely and capture differences in experiences between different groups – not just the “average”.
Averages can mask significant inequalities. As Paul Krugman put it, if Elon Musk walks into a bar then the average person there becomes a billionaire.
The unemployment[15] rate is at a 50-year low, and average household income[16] and wealth[17] at record levels. But not all Australians are sharing in this. The Indigenous unemployment rate, for example, is still about three times[18] the national average.
References
- ^ Measuring What Matters (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ from 2020 (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ from 2018 (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ has editorialised (www.theaustralian.com.au)
- ^ Chalmers 'measures what matters' – tracking our national wellbeing in 50 indicators (theconversation.com)
- ^ Josh Frydenberg (www.themonthly.com.au)
- ^ yoga mat and beads (twitter.com)
- ^ said a nation’s welfare (fraser.stlouisfed.org)
- ^ are all ahead (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ OECD (www.oecdbetterlifeindex.org)
- ^ wellbeing framework (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ Amartya Sen (www.nobelprize.org)
- ^ dropped in 2016 (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ approaches to measuring wellbeing (openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au)
- ^ unemployment (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ income (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ wealth (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ about three times (www.indigenoushpf.gov.au)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ statement (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ wellbeing of specific groups (theconversation.com)
- ^ Carer Wellbeing Survey (www.carersaustralia.com.au)
- ^ Regional Wellbeing Survey (www.regionalwellbeing.org.au)
- ^ wait longer to see a doctor (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ trust (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ Australians' national wellbeing shows a glass half full: Measuring What Matters report (theconversation.com)
- ^ iterative process (treasury.gov.au)
- ^ Australia's first wellbeing framework is about to measure what matters – but it's harder than counting GDP (theconversation.com)
















