Yes, Kate Middleton’s photo was doctored. But so are a lot of images we see today
- Written by T.J. Thomson, Senior Lecturer in Visual Communication & Digital Media, RMIT University
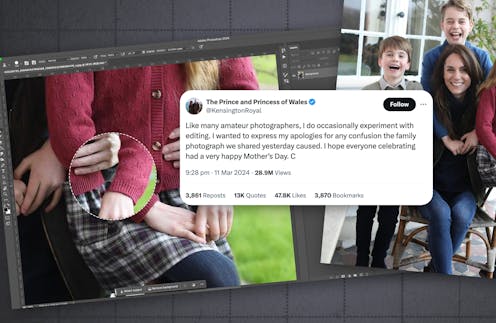
Rumours and conspiracies have been swirling[1] following the abdominal surgery and long recovery period of Catherine, Princess of Wales, earlier this year. They intensified on Monday when Kensington Palace released a photo of the princess with her three children.
The photo had clear signs of tampering, and international wire services withdrew the image[2] amid concerns around manipulation. The princess later apologised for any confusion[3] and said she had “experimented with editing” as many amateur photographers do.
Image editing is extremely common these days, and not all of it is for nefarious purposes. However, in an age of rampant misinformation, how can we stay vigilant around suspicious images?
What happened with the royal photo?
A close look reveals at least eight inconsistencies with the image.
Two of these relate to unnatural blur. Catherine’s right hand is unnaturally blurred, even though her left hand is sharp and at the same distance from the camera. The left side of Catherine’s hair is also unnaturally blurred, while the right side of her hair is sharp.
These types of edits are usually made with a blur tool that softens pixels. It is often used to make the background of an image less distracting or to smooth rough patches of texture.
Five of the edits appear to use the “clone stamp” tool. This is a Photoshop tool that takes part of the same or a different image and “stamps” it onto another part.
You can see this with the repeated pattern on Louis’s (on the left) sweater and the tile on the ground. You can also see it with the step behind Louis’s legs and on Charlotte’s hair and sleeve. The zipper on Catherine’s jacket also doesn’t line up.
The most charitable interpretation is that the princess was trying to remove distracting or unflattering elements. But the artefacts could also point to multiple images being blended together. This could either be to try to show the best version of each person (for example, with a smiling face and open eyes), or for another purpose.
How common are image edits?
Image editing is increasingly common as both photography and editing are increasingly becoming more automated.
This sometimes happens without you even knowing.
Take HDR (high dynamic range) images, for example. Point your iPhone or equivalent at a beautiful sunset and watch it capture the scene from the brightest highlights to the darkest shadows. What happens here is your camera makes multiple images and automatically stitches them together to make an image with a wider range of contrast[5].
While face-smoothing or teeth-whitening filters are nothing new, some smartphone camera apps apply them without being prompted. Newer technology like Google’s “Best Take” feature[6] can even combine the best attributes of multiple images to ensure everyone’s eyes are open and faces are smiling in group shots.
On social media, it seems everyone tries to show themselves in their best light, which is partially why so few of the photos on our camera rolls[7] make it onto our social media feeds. It is also why we often edit our photos to show our best sides.
But in other contexts, such as press photography, the rules are much stricter[8]. The Associated Press, for example, bans all edits beyond simple crops, colour adjustments, and “minor adjustments” that “restore the authentic nature of the photograph”.
Read more: Three images that show wartime photographs can have greater impact than the written word[9]
Professional photojournalists haven’t always gotten it right, though. While the majority of lens-based news workers adhere to ethical guidelines like those published by the National Press Photographers Association[10], others have let deadline pressures, competition and the desire for exceptional imagery cloud their judgement.
One such example was in 2017, when British photojournalist Souvid Datta admitted to visually plagiarising[11] another photographer’s work within his own composition.
Concerns around false or misleading visual information are at an all-time high, given advances in generative artificial intelligence (AI)[12]. In fact, this year the World Economic Forum named the risk of misinformation and disinformation as the world’s greatest short-term threat[13]. It placed this above armed conflict and natural disasters.
What to do if you’re unsure about an image you’ve found online
It can be hard to keep up with the more than 3 billion photos[14] that are shared each day.
But, for the ones that matter, we owe it to ourselves to slow down, zoom in and ask ourselves a few simple questions[15]:
1. Who made or shared the image? This can give clues about reliability and the purpose of making or sharing the image.
2. What’s the evidence? Can you find another version of the image, for example, using a reverse-image search engine[16]?
3. What do trusted sources say? Consult resources like AAP FactCheck[17] or AFP Fact Check[18] to see if authoritative sources have already weighed in.
Read more: Deepfakes: How to empower youth to fight the threat of misinformation and disinformation[19]
References
- ^ swirling (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ withdrew the image (apnews.com)
- ^ apologised for any confusion (twitter.com)
- ^ Photo by the Prince of Wales/Chart by T.J. Thomson (www.instagram.com)
- ^ with a wider range of contrast (www.adobe.com)
- ^ feature (blog.google)
- ^ camera rolls (www.tandfonline.com)
- ^ rules are much stricter (www.ap.org)
- ^ Three images that show wartime photographs can have greater impact than the written word (theconversation.com)
- ^ National Press Photographers Association (nppa.org)
- ^ visually plagiarising (time.com)
- ^ generative artificial intelligence (AI) (theconversation.com)
- ^ short-term threat (www.weforum.org)
- ^ 3 billion photos (theconversation.com)
- ^ questions (www.aap.com.au)
- ^ reverse-image search engine (tineye.com)
- ^ AAP FactCheck (www.aap.com.au)
- ^ AFP Fact Check (factcheck.afp.com)
- ^ Deepfakes: How to empower youth to fight the threat of misinformation and disinformation (theconversation.com)

















