The most endangered seals in the world once called Australia home
- Written by James Patrick Rule, Research Fellow, Monash University
Monk seals are one of the most endangered marine mammals alive today, with just over 2,000 individuals remaining in the wild. These seals live in warm waters, specifically the tropics and the Mediterranean.
Hunting by sailors in the past resulted in the extinction of the Caribbean monk seal[1] by the end of the 1950s. It also heavily reduced the numbers of the two remaining populations, in Hawaii and the Mediterranean.
Given how rare monk seals are today, it is hard to imagine a time when they were abundant. However, fossils from Australia show monk seals used to be much more widespread.
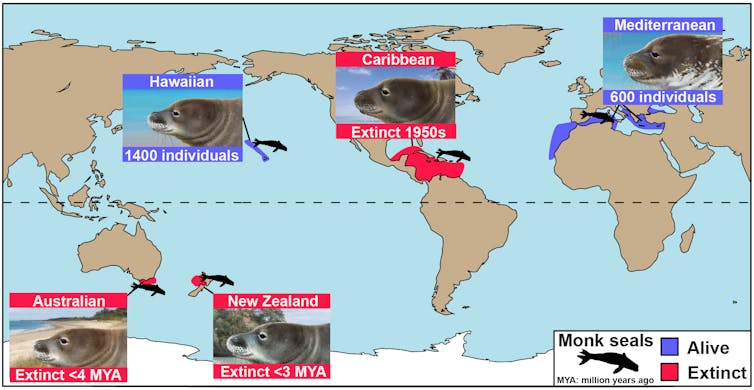 Monk seals only survive today in the Mediterranean and the tropics.
Peter Trusler, Author provided
Monk seals only survive today in the Mediterranean and the tropics.
Peter Trusler, Author provided
Two fossils from Beaumaris and Hamilton in Victoria have turned out to be the remains of ancient monk seals. This discovery, part of an ongoing effort to investigate Melbourne’s globally important marine fossils[2], was outlined by our team in a paper published in the Journal of Systematic Palaeontology[3].
How are monk seals different from other seals?
Monk seals are from a completely different group[4] to the fur seals and sea lions that live in Australian waters today. Australia’s warm environment in the past made it an ideal habitat for true seals[5], the group to which monk seals belong.
These seals would have coexisted with Australia’s ancient megafauna, such as giant kangaroos[6] and the oddball palorchestids[7].
Read more: In a land of ancient giants, these small oddball seals once called Australia home[8]
This discovery was made when our team revisited two fossils from Museums Victoria’s collections, the identity of which has been a mystery for 40 years.
When we analysed them, they turned out to be the oldest evidence of monk seals found so far, at roughly 5 million years old. The fossils are earbones, the part of the skull that contains the structures needed for hearing. The anatomy of earbones means they are very useful for helping palaeontologists identify what animal fossils belong to.
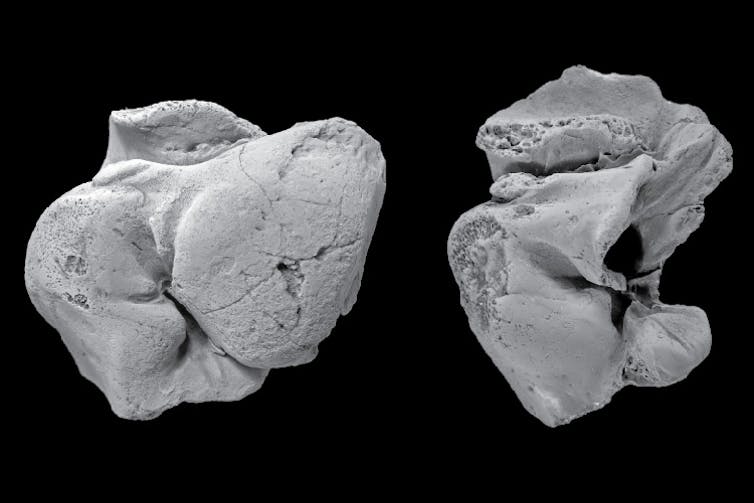 Ancient fossils found at Beaumaris and Hamilton in Victoria, Australia, belong to 5 million year old monk seals.
Erich Fitzgerald, Author provided
Ancient fossils found at Beaumaris and Hamilton in Victoria, Australia, belong to 5 million year old monk seals.
Erich Fitzgerald, Author provided
Together with the recently discovered Eomonachus (a 3 million-year-old New Zealand monk seal[9]), these fossils demonstrate that monk seals had a long history in Australasia. These discoveries have now almost doubled the number of geographic regions monk seals used to occupy in the past, and confirm they used to be a much larger group.
What happened?
If monk seals were so widespread down under in the past, why are they no longer here? The short answer is climate change.
Around 2.5 million years ago, the onset of the ice ages changed the world’s oceans, making the waters colder and sea levels lower. This led to extinctions[10] in many marine mammal groups, including the monk seals. In short, monk seals disappeared in the southern hemisphere, leaving them only present in the Mediterranean and the tropics.
Read more: Scientists thought these seals evolved in the north. 3-million-year-old fossils from New Zealand suggest otherwise[11]
Despite monk seals being protected from hunting today, these fossil discoveries suggest their troubles may be far from over. Their fossil relatives have now demonstrated they are susceptible to environmental change.
Rising sea levels are already threatening the Hawaiian species[12], and human-driven changes also endanger the Mediterranean species[13].
Without continued protection, the remaining monk seals may soon disappear along with their extinct relatives.
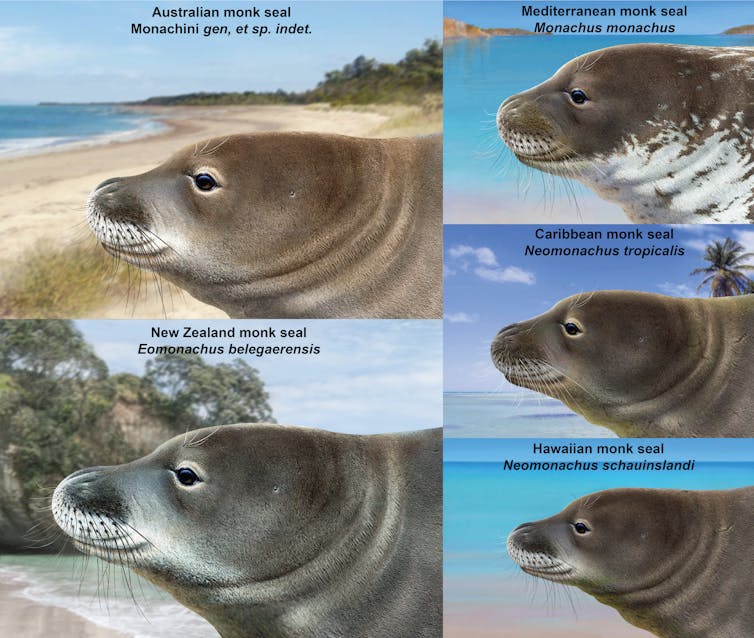 This illustration shows reconstructions of fossil monk seals and their modern relatives.
Peter Trusler, Author provided
This illustration shows reconstructions of fossil monk seals and their modern relatives.
Peter Trusler, Author provided
References
- ^ extinction of the Caribbean monk seal (www.sciencedaily.com)
- ^ Melbourne’s globally important marine fossils (museumsvictoria.com.au)
- ^ Journal of Systematic Palaeontology (www.tandfonline.com)
- ^ different group (lens.monash.edu)
- ^ ideal habitat for true seals (theconversation.com)
- ^ giant kangaroos (www.newscientist.com)
- ^ oddball palorchestids (cosmosmagazine.com)
- ^ In a land of ancient giants, these small oddball seals once called Australia home (theconversation.com)
- ^ a 3 million-year-old New Zealand monk seal (theconversation.com)
- ^ led to extinctions (www.popsci.com)
- ^ Scientists thought these seals evolved in the north. 3-million-year-old fossils from New Zealand suggest otherwise (theconversation.com)
- ^ already threatening the Hawaiian species (earthjustice.org)
- ^ endanger the Mediterranean species (monachus-guardian.org)
Read more https://theconversation.com/the-most-endangered-seals-in-the-world-once-called-australia-home-162523

















