Australia's quarantine system needs a smarter design
- Written by Mathew Aitchison, Professor of Architecture and CEO of Building 4.0 CRC, Monash University
The announcement[1] that the Victorian and federal governments will build a 1,000-bed COVID quarantine hub at Mickleham in Melbourne’s north marks a welcome end, or at least a fresh chapter, to the finger-pointing over Australia’s quarantine saga.
Time is of the essence when protecting Australians from COVID, so hats off to both governments for setting an ambitious timeline that could see the facility up and running by the end of this year.
But in their haste to deliver an alternative to hotel quarantine, we believe the governments haven’t taken advantage of the newest available innovations.
The plan[2] for the proposed quarantine facility produced by the Victorian government is, by its own admission, little more than a specced-up version of a mining camp, similar to the Howard Springs facility already in use in the Northern Territory. In turn, this type of construction harks back to the postwar quarantine facilities built from the 1950s onwards.
Part of the problem with the current proposal is the focus on the “hardware”, with almost no discussion of the “software”. By hardware, we mean buildings, physical structures, road layouts and infrastructure; by software, we mean how it will be used, the operational patterns and processes, and “softer” operational modes of use and their technologies.
This hardware-centric approach would be more reassuring if the hardware were the best and fittest for use, but unfortunately the proposal has reached for what it knows, and what it knows is around 70 years old.
A smarter way
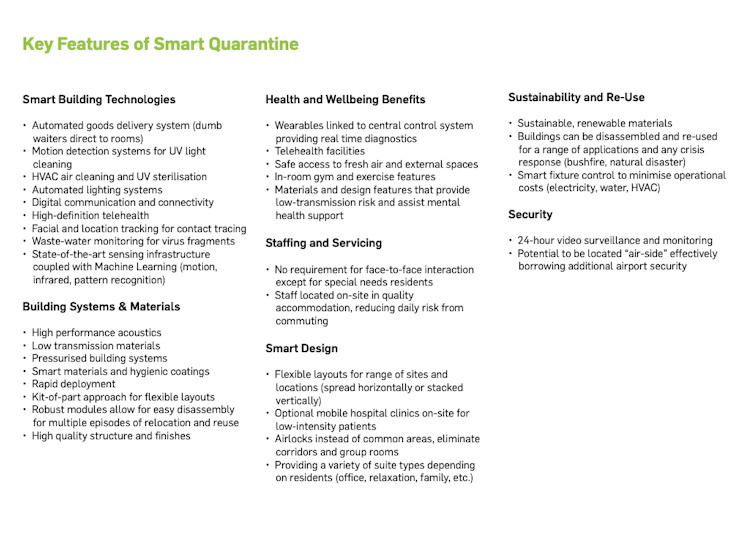
We and our colleagues at the Building 4.0 Cooperative Research Centre[3], funded jointly by the federal government and a consortium of industry, are developing a state-of-the-art design, called Q_Smart[4], which we submitted to the Victorian government in March 2021.
In our proposal, building services, controls, sensors and management systems (alongside well-designed and efficiently produced buildings) all play a role in preventing the transmission of COVID-19. We might think of this as a correction towards a more “software-driven” approach, as it seeks to use a range of processes, techniques and technologies[5] already available from our collaborators at Siemens to augment the work done by the physical structures.
In terms of the physical layout, our design avoids the large common corridors, inadequate air-tightness controls for rooms, or unhygienic air handling systems that have emerged as problems with current hotel stock.
 Building 4.0 CRC[6]
As leading infection control experts have already pointed out[7], mining dongas may have worked well so far for quarantine at the repurposed Howard Springs facility in the Northern Territory. But from an epidemiological point of view, the current design is concerning for the proximity of neighbouring verandahs, especially in cases where more than one group of quarantine residents is housed in a unit.
The government’s provisional staffing patterns for the new facility suggests that separation between residents will rely on strict protocols around staff movements and quarantine measures intended to slow and limit the spread of disease, should a breach occur.
Read more:
This is how we should build and staff Victoria's new quarantine facility, say two infection control experts[8]
In contrast, the smart building management system we are developing would not “wait” for a breach to occur, but would aim to stop such contact ever being made. A door would not open, an airlock would have its contents automatically evacuated, and UV light would cleanse contaminated surfaces or air in ducting.
Some of these features, such as proximity authentication, are innovations that we routinely expect from our 20-year-old cars. If we turn to our now ubiquitous smartphones, there are yet further possibilities to safely and conveniently track and control movement in more humane way that would not need to reach for punitive ankle bracelets and the like. And, yes, should a breach occur, such systems could ultimately carry out near-instantaneous contact-tracing.
But such a system could only work if the “hardware” and “software” are fully integrated and planned together from the start.
An eye on the future
There are many ways to deal with quarantine, and although it may be too late to integrate our designs into the proposed Victorian facility, perhaps other states and territories embarking on building ventures might yet consider this advice.
In viewing the current proposed plan of closely spaced mining dongas, arranged in “mini-districts”, it is nigh-on impossible to imagine it being used for anything other than a quarantine facility, or perhaps a correctional centre.
Building 4.0 CRC[6]
As leading infection control experts have already pointed out[7], mining dongas may have worked well so far for quarantine at the repurposed Howard Springs facility in the Northern Territory. But from an epidemiological point of view, the current design is concerning for the proximity of neighbouring verandahs, especially in cases where more than one group of quarantine residents is housed in a unit.
The government’s provisional staffing patterns for the new facility suggests that separation between residents will rely on strict protocols around staff movements and quarantine measures intended to slow and limit the spread of disease, should a breach occur.
Read more:
This is how we should build and staff Victoria's new quarantine facility, say two infection control experts[8]
In contrast, the smart building management system we are developing would not “wait” for a breach to occur, but would aim to stop such contact ever being made. A door would not open, an airlock would have its contents automatically evacuated, and UV light would cleanse contaminated surfaces or air in ducting.
Some of these features, such as proximity authentication, are innovations that we routinely expect from our 20-year-old cars. If we turn to our now ubiquitous smartphones, there are yet further possibilities to safely and conveniently track and control movement in more humane way that would not need to reach for punitive ankle bracelets and the like. And, yes, should a breach occur, such systems could ultimately carry out near-instantaneous contact-tracing.
But such a system could only work if the “hardware” and “software” are fully integrated and planned together from the start.
An eye on the future
There are many ways to deal with quarantine, and although it may be too late to integrate our designs into the proposed Victorian facility, perhaps other states and territories embarking on building ventures might yet consider this advice.
In viewing the current proposed plan of closely spaced mining dongas, arranged in “mini-districts”, it is nigh-on impossible to imagine it being used for anything other than a quarantine facility, or perhaps a correctional centre.
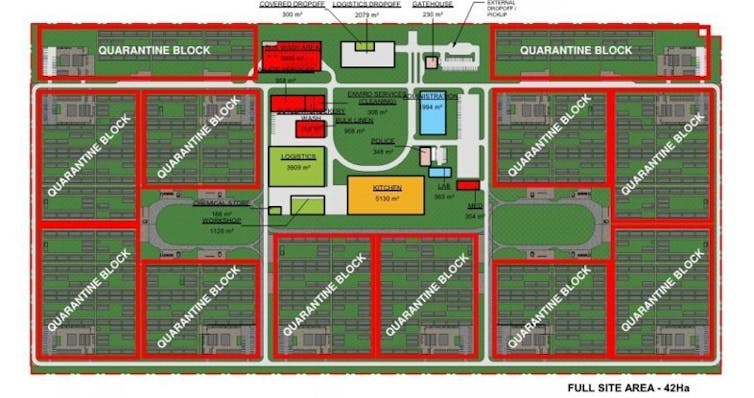 The plan for the proposed quarantine hub makes it hard to imagine it being used for anything other than quarantine - or perhaps a correctional facility.
Vic.gov.au
Read more:
Hotel quarantine causes 1 outbreak for every 204 infected travellers. It's far from ‘fit for purpose’[9]
Q_Smart, on the other hand, was designed to be flexible, reusable and adaptable to different sites, which, for example, may not necessarily have large amounts of flat open space. This would potentially allow facilities built for quarantine to be reused for other purposes after the pandemic. Transforming the building’s operational pattern would be a matter of simply flipping a few (virtual) switches. Depending on the use case, certain controls could be activated or deactivated, new patterns of movement through the buildings could be enabled or disabled almost instantaneously.
With more thinking and development, perhaps such buildings could also be used as affordable housing, or disaster relief accommodation or — how’s this for ironic — future hotels.
This article was coauthored by Dr Bronwyn Evans AM[10], chair of Building 4.0 CRC[11] and chief executive of Engineers Australia[12].
The plan for the proposed quarantine hub makes it hard to imagine it being used for anything other than quarantine - or perhaps a correctional facility.
Vic.gov.au
Read more:
Hotel quarantine causes 1 outbreak for every 204 infected travellers. It's far from ‘fit for purpose’[9]
Q_Smart, on the other hand, was designed to be flexible, reusable and adaptable to different sites, which, for example, may not necessarily have large amounts of flat open space. This would potentially allow facilities built for quarantine to be reused for other purposes after the pandemic. Transforming the building’s operational pattern would be a matter of simply flipping a few (virtual) switches. Depending on the use case, certain controls could be activated or deactivated, new patterns of movement through the buildings could be enabled or disabled almost instantaneously.
With more thinking and development, perhaps such buildings could also be used as affordable housing, or disaster relief accommodation or — how’s this for ironic — future hotels.
This article was coauthored by Dr Bronwyn Evans AM[10], chair of Building 4.0 CRC[11] and chief executive of Engineers Australia[12].
References
- ^ announcement (www.theage.com.au)
- ^ plan (www.vic.gov.au)
- ^ Building 4.0 Cooperative Research Centre (building4pointzero.org)
- ^ Q_Smart (building4pointzero.org)
- ^ range of processes, techniques and technologies (www.linkedin.com)
- ^ Building 4.0 CRC (building4pointzero.org)
- ^ already pointed out (theconversation.com)
- ^ This is how we should build and staff Victoria's new quarantine facility, say two infection control experts (theconversation.com)
- ^ Hotel quarantine causes 1 outbreak for every 204 infected travellers. It's far from ‘fit for purpose’ (theconversation.com)
- ^ Dr Bronwyn Evans AM (building4pointzero.org)
- ^ Building 4.0 CRC (building4pointzero.org)
- ^ Engineers Australia (www.engineersaustralia.org.au)

















