A mysterious interstellar radio signal has been blinking on and off every 22 minutes for over 30 years
- Written by Natasha Hurley-Walker, Radio Astronomer, Curtin University
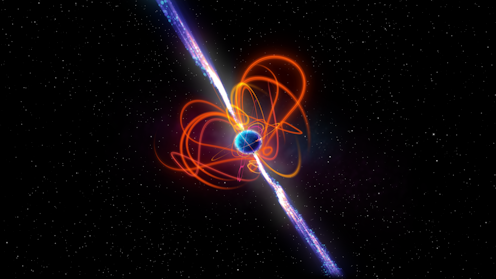
Last year, we made an intriguing discovery – a radio signal in space that switched on and off every 18 minutes[1].
Astronomers expect to see some repeating radio signals in space, but they usually blink on and off much more quickly. The most common repeating signals come from pulsars, rotating neutron stars that emit energetic beams like lighthouses, causing them to blink on and off as they rotate towards and away from the Earth.
Pulsars slow down as they get older, and their pulses become fainter, until eventually they stop producing radio waves altogether. Our unusually slow pulsar could best be explained as a magnetar – a pulsar with exceedingly complex and powerful magnetic fields that could generate radio waves for several months before stopping.
Unfortunately, we detected the source using data gathered in 2018. By the time we analysed the data and discovered what we thought might be a magnetar it was 2020, and it was no longer producing radio waves. Without additional data, we were unable to test our magnetar theory.
Nothing new under the sun
Our Universe is vast, and so far every new phenomenon we’ve discovered has not been unique. We knew that if we looked again, with well-designed observations, we had a good chance of finding another long-period radio source.
So, we used the Murchison Widefield Array radio telescope in Western Australia to scan our Milky Way galaxy every three nights for several months.
We didn’t need to wait long. Almost as soon as we started looking, we found a new source, in a different part of the sky, this time repeating every 22 minutes.
At last, the moment we had been waiting for. We used every telescope we could find, across radio, X-ray, and optical light, making as many observations as possible, assuming it would not be active for long. The pulses lasted five minutes each, with gaps of 17 minutes between. Our object looked a lot like a pulsar, but spinning 1,000 times slower.
The newly discovered mystery object emits pulses of radio waves in a 22-minute cycle.Hiding in plain sight
The real surprise came when we searched the oldest radio observations of this part of the sky. The Very Large Array in New Mexico, United States, has the longest-running archive of data. We found pulses from the source in data from every year we looked – the oldest one in an observation made in 1988.
Observing over three decades meant we could precisely time the pulses. The source is producing them like clockwork, every 1,318.1957 seconds, give or take a tenth of a millisecond.
According to our current theories, for the source to be producing radio waves, it should be slowing down. But according to the observations, it is not.
In our article in Nature[2], we show that the source lies “below the death line”, which is the theoretical limit of how neutron stars generate radio waves; this holds even for quite complex magnetic field models. Not only that, but if the source is a magnetar, the radio emission should only be visible for a few months to years – not 33 years and counting.
So when we tried to solve one problem, we accidentally created another. What are these mysterious repeating radio sources?
What about ET?
Of course, it’s very tempting at this point to reach to extraterrestrial intelligence as an option. The same thing happened when pulsars were discovered: astrophysicist Jocelyn Bell Burnell and her colleagues, who found the first pulsar, nicknamed it “LGM 1”, for “Little Green Men 1”.
But as soon as Bell and her colleagues made further detections, they knew it could not be aliens. It would be incredibly unlikely for so many similar signals to be coming from so many different parts of the sky.
The pulses, similar to those of our source, contained no information, just “noise” across all frequencies, just like natural radio sources. Also, the energy requirements to emit a signal at all frequencies are staggering: you need to use, well, a neutron star.
While it’s tempting to try to explain a new phenomenon this way, it’s a bit of a cop out. It doesn’t encourage us to keep thinking, observing and testing new ideas. I call it the “aliens of the gaps[3]” approach.
Fortunately, this source is still active, so anyone in the world can observe it. Perhaps with creative follow-up observations, and more analysis, we’ll be able to solve this new cosmic mystery.
References
- ^ every 18 minutes (theconversation.com)
- ^ article in Nature (www.nature.com)
- ^ aliens of the gaps (en.wikipedia.org)
















