Pest plants and animals cost Australia around $25 billion a year – and it will get worse
- Written by Corey J. A. Bradshaw, Matthew Flinders Professor of Global Ecology and Models Theme Leader for the ARC Centre of Excellence for Australian Biodiversity and Heritage, Flinders University
Shamefully, Australia has one of the highest extinction rates[1] in the world. And the number one[2] threat to our species is invasive or “alien” plants and animals.
But invasive species don’t just cause extinctions and biodiversity loss – they also create a serious economic burden. Our research[3], published today, reveals invasive species have cost the Australian economy at least A$390 billion in the last 60 years alone.
Our paper – the most detailed assessment of its type ever published in this country – also reveals feral cats are the worst invasive species in terms of total costs, followed by rabbits and fire ants.
Without urgent action, Australia will continue to lose billions of dollars every year on invasive species.
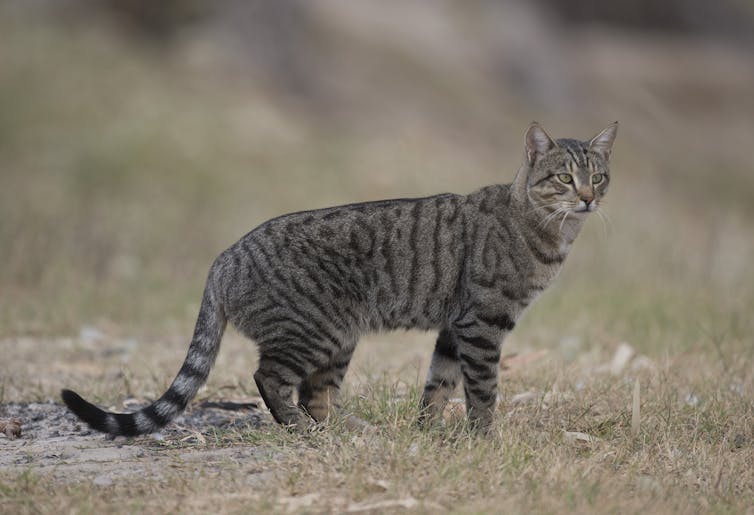 Feral cats are Australia’s costliest invasive species.
Adobe Stock/240188862
Feral cats are Australia’s costliest invasive species.
Adobe Stock/240188862
Huge economic burden
Invasive species are those not native to a particular ecosystem. They are introduced either by accident or on purpose and become pests.
Some costs involve direct damage to agriculture, such as insects or fungi destroying fruit. Other examples include measures to control invasive species like feral cats and cane toads, such as paying field staff and buying fuel, ammunition, traps and poisons.
Our previous research put the global cost of invasive species at A$1.7 trillion[4]. But this is most certainly a gross underestimate because so many data are missing.
Read more: Attack of the alien invaders: pest plants and animals leave a frightening $1.7 trillion bill[5]
As a wealthy nation, Australia has accumulated more reliable cost data than most other regions. These costs have increased exponentially over time – up to sixfold each decade since the 1970s.
We found invasive species now cost Australia around A$24.5 billion a year, or an average 1.26% of the nation’s gross domestic product[6]. The costs total at least A$390 billion in the past 60 years.
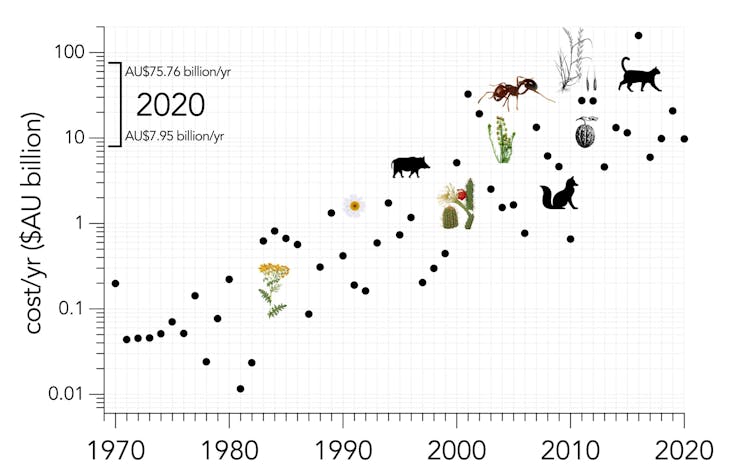 Increase in annual costs of invasive species in Australia from 1960 to 2020. The predicted range for 2020 is shown in the upper left quadrant. Note the logarithmic scale of the vertical axis.
CJA Bradshaw
Increase in annual costs of invasive species in Australia from 1960 to 2020. The predicted range for 2020 is shown in the upper left quadrant. Note the logarithmic scale of the vertical axis.
CJA Bradshaw
Worst of the worst
Our analysis found feral cats have been the most economically costly species since 1960. Their A$18.7 billion bill is mainly associated with attempts to control their abundance and access, such as fencing, trapping, baiting and shooting.
Feral cats are a main driver[7] of extinctions in Australia, and so perhaps investment to limit their damage is worth the price tag.
 Tasmania’s bane — ragwort (Senecio jacobaea)
Adobe Stock/157770032
Tasmania’s bane — ragwort (Senecio jacobaea)
Adobe Stock/157770032
As a group, the management and control of invasive plants proved the worst of all, collectively costing about A$200 billion. Of these, annual ryegrass[8], parthenium[9] and ragwort[10] were the costliest culprits because of the great effort needed to eradicate them from croplands.
Invasive mammals were the next biggest burdens, costing Australia A$63 billion.
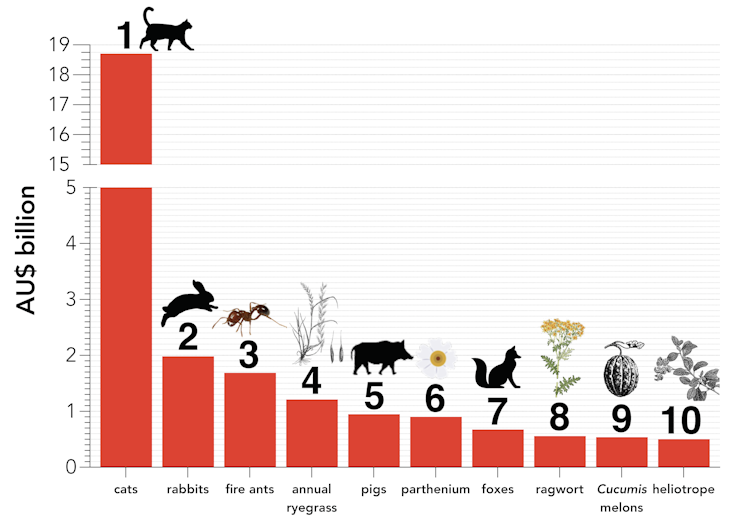 The 10 costliest invasive species in Australia.
CJA Bradshaw
The 10 costliest invasive species in Australia.
CJA Bradshaw
Variation across regions
For costs that can be attributed to particular states or territories, New South Wales had the highest costs, followed by Western Australia then Victoria.
Red imported fire ants[11] are the costliest species in Queensland, and ragwort is the economic bane of Tasmania.
The common heliotrope[12] is the costliest species in both South Australia and Victoria, and annual ryegrass tops the list in WA.
In the Northern Territory, the dothideomycete[13] fungus that causes banana freckle disease[14] brings the greatest economic burden, whereas cats and foxes[15] are the costliest species in the ACT and NSW.
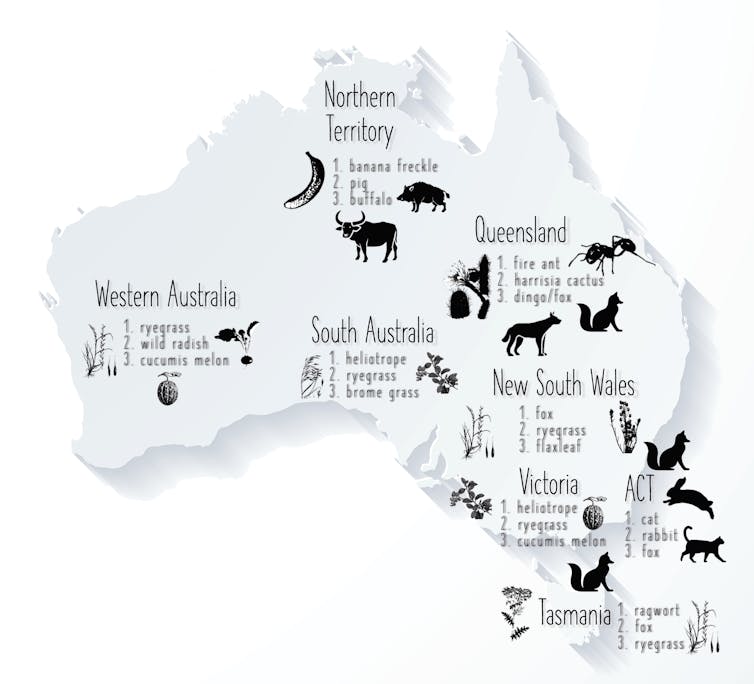 The three costliest species by Australian state/territory.
CJA Bradshaw
The three costliest species by Australian state/territory.
CJA Bradshaw
Better assessments needed
Our study is one of 19 region-specific analyses released today[16]. Because the message about invasive species must get out to as many people as possible, our article’s abstract was translated into 24 languages[17].
This includes Pitjantjatjara[18], a widely spoken Indigenous language[19].
Read more: Australia’s threatened species plan has failed on several counts. Without change, more extinctions are assured[20]
Even the massive costs we reported are an underestimate. This is because of we haven’t yet surveyed all the places these species occur, and there is a lack of standardised reporting by management authorities and other agencies.
For example, our database lists several fungal plant pathogens. But no cost data exist for some of the worst offenders, such as the widespread Phytophthora cinnamomi pathogen that causes major crop losses and damage to biodiversity[21].
Developing better methods[22] to estimate the environmental impacts of invasive species, and the benefit of management actions, will allow us to use limited resources more efficiently.
 Phytophthora cinnamomi, a widespread, but largely uncosted, fungal pathogen.
Adobe Stock/272252666
Phytophthora cinnamomi, a widespread, but largely uncosted, fungal pathogen.
Adobe Stock/272252666
A constant threat
 Fall armyworm, a major crop pest.
Adobe Stock/335450066
Fall armyworm, a major crop pest.
Adobe Stock/335450066
Many species damaging to agriculture[23] and the environment[24] are yet to make it to our shores.
The recent arrival in Australia of fall armyworm, a major agriculture pest[25], reminds us how invasive species will continue their spread[26] here and elsewhere.
As well as the economic damage, invasive species also bring intangible costs[27] we have yet to measure adequately. These include the true extent of ecological damage, human health consequences, erosion of ecosystem services and the loss of cultural values.
Without better data, increased investment, a stronger biosecurity system and interventions such as animal culls, invasive species will continue to wreak havoc across Australia.
The authors acknowledge the Traditional Owners of the lands on which they did this research.
Ngadlu tampinthi yalaka ngadlu Kaurna yartangka inparrinthi. Ngadludlu tampinthi, parnaku tuwila yartangka.
References
- ^ highest extinction rates (theconversation.com)
- ^ number one (theconversation.com)
- ^ research (doi.org)
- ^ A$1.7 trillion (theconversation.com)
- ^ Attack of the alien invaders: pest plants and animals leave a frightening $1.7 trillion bill (theconversation.com)
- ^ gross domestic product (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ main driver (theconversation.com)
- ^ annual ryegrass (www.agric.wa.gov.au)
- ^ parthenium (weeds.dpi.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ ragwort (dpipwe.tas.gov.au)
- ^ Red imported fire ants (www.daf.qld.gov.au)
- ^ common heliotrope (weedsofmelbourne.org)
- ^ dothideomycete (dothideomycetes.org)
- ^ banana freckle disease (nt.gov.au)
- ^ foxes (www.environment.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ released today (doi.org)
- ^ 24 languages (doi.org)
- ^ Pitjantjatjara (omniglot.com)
- ^ a widely spoken Indigenous language (www.welcometocountry.org)
- ^ Australia’s threatened species plan has failed on several counts. Without change, more extinctions are assured (theconversation.com)
- ^ crop losses and damage to biodiversity (doi.org)
- ^ better methods (news.microsoft.com)
- ^ agriculture (www.agriculture.gov.au)
- ^ environment (www.agriculture.gov.au)
- ^ a major agriculture pest (www.agriculture.gov.au)
- ^ continue their spread (doi.org)
- ^ intangible costs (doi.org)

















