Opening with 70% of adults vaccinated, the Doherty report predicts 1.5K deaths in 6 months. We need a revised plan
- Written by Stephen Duckett, Director, Health and Aged Care Program, Grattan Institute
One consequence of the escalating COVID outbreak in New South Wales has been increased political tension around the “national plan” for COVID reopening.
The prime minister has argued[1] that states signed up to the plan – albeit “in principle”, whatever that means – and they should do whatever the plan says, whenever the plan says to do it.
Some premiers are now pushing back[2], arguing the Doherty Institute modelling was based on certain assumptions which no longer hold true so the previous agreement no longer stands.
There are three distinct questions at issue here. Is the Doherty Institute modelling still applicable? How does the national plan stack up? And what should happen next?
1. Is the Doherty Institute modelling still applicable?
The Doherty Institute was given a very specific remit[3]. It was asked “to define a target level of vaccine coverage for transition to Phase B of the national plan”, where lockdowns would be “less likely, but possible”.
Read more: Australia has a new four-phase plan for a return to normality. Here's what we know so far[4]
In identifying the vaccination coverage target for the transition to Phase B, Doherty’s experts assumed that testing, tracing, isolation, and quarantine (TTIQ), would be central to maintaining lower case numbers.
They highlighted two scenarios in terms of testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine capacity – an “optimal” scenario and a “partially effective” scenario – summarised in the table below.
Doherty Institute modelling outcomes
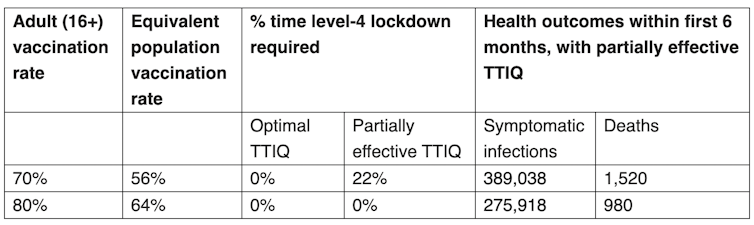 TTIQ = testing, tracing, isolation, and quarantine. This assumes an all adults vaccination allocation strategy.
Doherty Institute
TTIQ = testing, tracing, isolation, and quarantine. This assumes an all adults vaccination allocation strategy.
Doherty Institute
While these numbers may look acceptable, the assumptions underlying them are now hanging by a thread.
Case numbers have been rising rapidly[5], putting significant pressure on testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine capacity.
Doherty Institute described its assumptions thus:
We assume that once community transmission becomes established leading to high caseloads, TTIQ [testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine] is less efficacious than the optimal levels observed in Australia because public health response capacity is finite.
This tells us that given our current high case numbers, we can probably only assume, at best, “partially effective” testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine capacity.
It’s also important to note the Doherty modelling did not incorporate scenarios where the virus was in uncontrolled spread after target vaccination levels are achieved.
But it now seems unlikely that NSW – and maybe even Victoria – will be able to suppress COVID down to zero before any vaccination target is reached.
If lockdowns are eased according to the modelled targets, while there is still substantial community transmission, testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine is unlikely to be enough to suppress further spread sufficiently, potentially resulting in higher numbers of hospitalisations and deaths than initially modelled.
2. How does the national plan stack-up?
The federal government used the Doherty Institute report’s findings as the basis of the “national plan[6]” it put to National Cabinet.
But it glossed over the options, scenarios, and caveats in the Doherty modelling, and assumed the most optimistic testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine scenario: that everything would be rosy if Australia started opening up once 70% of adults (equivalent to only just over half the population) are vaccinated.
Read more: National Cabinet's plan out of COVID aims too low on vaccinations and leaves crucial questions unanswered[7]
The transition to Phase C, where lockdowns would be targeted and vaccinated people would be exempt from restrictions, was also optimistically adopted at 80% adult vaccination, despite the lack of modelling for this scenario in the Doherty report.
In a bid to make it appear convincing – but also realistic, given all the uncertainty – a veil of vagueness[8] was cast over the national plan. The document is full of weasel-words and caveats, which means it is impossible for anyone to be held to account.
The equivocal “in-principle” condition on National Cabinet’s approval[9] makes it even harder to know exactly what premiers signed up to.
But the severity of the New South Wales outbreak has forced some of our leaders to take off the rose-coloured glasses and adopt a more realistic view. Premiers are now saying they did not sign up to high death tolls.
According to Doherty modelling, deaths could reach 1,500 within six months of implementing Phase B. Agreeing to such a scenario is politically untenable for states that currently have zero cases.
3. So, what should happen next?
With states divided over the national plan, and the modelling potentially out of date, it’s time for National Cabinet to come back with a new approach. We need a revised national plan – one that all states can sign up to, one that is not full of caveats and conditions.
This should include a realistic plan for scaling up testing-tracing-isolation-quarantine capacity so that it can manage in a feasible way when each infected person could have at least ten new contacts per day.
And it should include a plan to protect primary schools and childcare centres while a vaccine remains unavailable for younger children.
Grattan Institute has also done its own modelling[10].
But our model was about Phase D – what Australia needs to do to avoid obtrusive restrictions such as lockdowns altogether – which was not modelled by the Doherty Institute.
We argued that it is only safe to open the borders, to lift restrictions, and to manage without lockdowns and use only unobtrusive measures such as masks on public transport, if we vaccinate at least 80% of the total population and continue the vaccination rollout to 90% throughout 2022.
Recent modelling from other academics[11] has come to similar conclusions, with some even suggesting a slightly higher threshold for safe re-opening.
Governments cannot keep making unrealistic promises about easing restrictions at 70% and 80% adult vaccination, a plan that relied on optimistic scenarios in the first place, and one that now bears little relation to the real world. It is irresponsible to build public momentum and hope around targets that are unlikely going to be enough.
Australia needs the National Cabinet to come clean and accept that the changing circumstances require a change in the plan.
References
- ^ prime minister has argued (www.news.com.au)
- ^ Some premiers are now pushing back (thewest.com.au)
- ^ Doherty Institute was given a very specific remit (www.doherty.edu.au)
- ^ Australia has a new four-phase plan for a return to normality. Here's what we know so far (theconversation.com)
- ^ Case numbers have been rising rapidly (www.health.gov.au)
- ^ national plan (www.pm.gov.au)
- ^ National Cabinet's plan out of COVID aims too low on vaccinations and leaves crucial questions unanswered (theconversation.com)
- ^ veil of vagueness (openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au)
- ^ equivocal “in-principle” condition on National Cabinet’s approval (www.pm.gov.au)
- ^ its own modelling (grattan.edu.au)
- ^ modelling from other academics (osf.io)

















