COVID halved international student numbers in Australia. The risk now is we lose future skilled workers and citizens
- Written by Nancy Arthur, Dean of Research, UniSA Business, University of South Australia
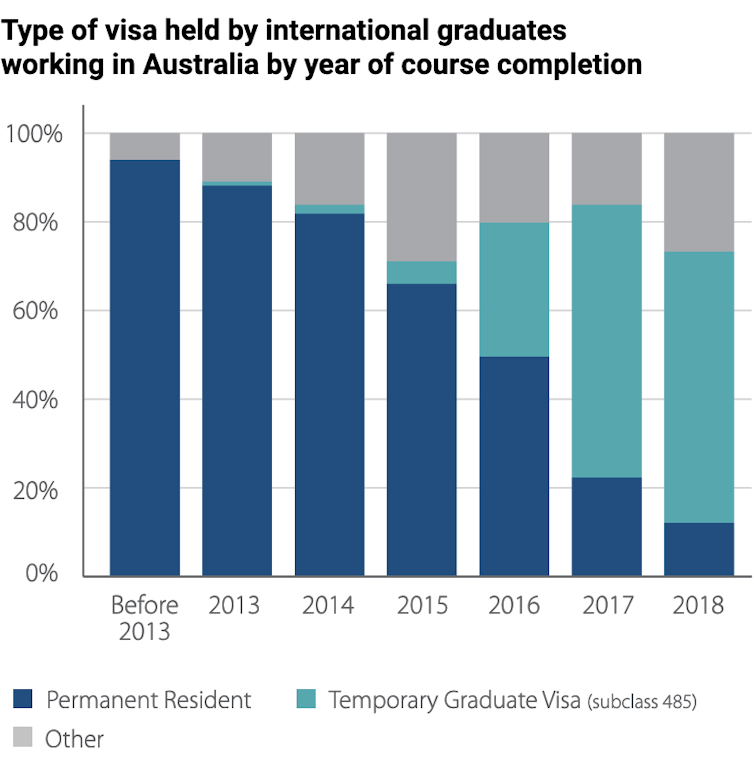
The saying “you don’t know what you’ve got ’til it’s gone” reminds us not to take things for granted. It is often when we no longer have something or someone that we recognise the value of what we’ve lost. This is true of international students in Australia whose numbers halved[1] during the pandemic.
Can hindsight help us understand what we had and help to guide our future? That question lingers as tens of thousands[2] of new and returning international students arrive back in Australia now that borders have reopened.
Read more: Border opening spurs rebound in demand from international students[3]
Students pursue international education for a variety of reasons. The main one is to improve their employment prospects.
International students are looking for high-quality, relevant curriculum and credentials that will best serve their career plans. While studying, they also seek social connections that help them to navigate local education and employment systems.
The pandemic created chaos and uncertainty about enrolments, border closures, flight availability and quarantine requirements. Over the past two years, many international students had to put their plans on hold. They hung on to the possibility of studying and working in Australia.
Let’s not forget, they can choose other countries that will be seeking highly educated and skilled graduates. Some have already moved on to countries where borders were open, such as Canada. These countries offered access to high-quality international education with fewer complications and greater certainty about transitioning to work visas.
Read more: International student numbers hit record highs in Canada, UK and US as falls continue in Australia and NZ[4]
Their absence hit us hard
Consider what Australia lost when so many international students were gone. In 2019, they contributed an estimated $40.3 billion[5] to the economy. International education supported about 250,000 jobs[6] in Australia.
Border closures reduced enrolments by up to 70%[7] in some parts of the higher education sector.
Read more: Australia's multilingual identity is an asset for selling our English-language teaching to the world[8]
The financial impacts on Australian universities have been smaller than originally predicted, but the loss of billions in revenue should not be discounted. Universities were exposed to the risks of depending on a never-ending flow of new international students and their tuition fees. The pandemic’s impacts on university finances[9] led to the loss of as many as 35,000 academic and professional jobs[10].
Local communities and businesses also missed the consumer power of international students and visiting family members who purchased goods and services. Employers have struggled to find enough local workers for job vacancies that these students would fill.
Australia must extend the welcome mat
The Australian government recently announced incentives[11] for international students to return soon to help overcome labour shortages and stimulate market growth. Visa fee rebates and relaxed restrictions on allowable working hours are aimed at recovery in the international student market, while filling gaps in the workforce. What remains to be seen is how well entry-level and part-time jobs in service and hospitality will translate into future employment opportunities that match these students’ qualifications.
The fall in international student numbers also meant losing key resources for intercultural learning. Although many of us are longing to travel abroad for a dose of intercultural exposure, learning at home between local and international students is a relatively untapped resource. Increasing the numbers of international and local students studying together is part of the solution identified by the Australian Strategy for International Education[12].
Read more: Australia's strategy to revive international education is right to aim for more diversity[13]
Many international students will need extra support to develop social capital[14] – the friendships, community contacts, mentors and networks that help to build a sense of belonging now and in the future.
International students have been treated like commodities for higher education and the labour market. But they are people, whose choice of international education is connected to their hopes and plans after graduating.
The global pursuit of talent will increase graduates’ opportunities to decide which country they choose for education, for employment and for permanent migration. Not every international graduate will choose to stay in Australia. Fluctuating immigration policy makes it difficult to predict who will be allowed to stay and who will not.

















