The push for 'researcher entrepreneurs' could be a step backward for gender equity
- Written by Caroline Schuster, Senior Lecturer, School of Archaeology and Anthropology; Director, Australian National Centre for Latin American Studies, Australian National University
Scott Morrison recently announced[1] a $2.2 billion Research Commercialisation Action Plan[2] for the next ten years. The plan centres on a competitive grant scheme to promote start-ups and industry partnerships. The prime minister’s message to universities was clear:
“we need to find and develop a new breed of researcher entrepreneurs in Australia”.
The statement came on the heels of a letter of expectations[3] from the acting minister for education and youth to the Australian Research Council in which he encouraged greater collaboration with industry, particularly the manufacturing sector.
Read more: Latest government bid to dictate research directions builds on a decade of failure[4]
What might we expect from the rise of researcher entrepreneurs in Australian universities? Who are likely to be seen as exemplars of this new breed?
Given the male-dominated makeup of the industry partners who are meant to lead the commercialisation of research, what we might realistically expect is a major step backward for gender equity in Australian universities.
Industry stakeholders’ gender gap
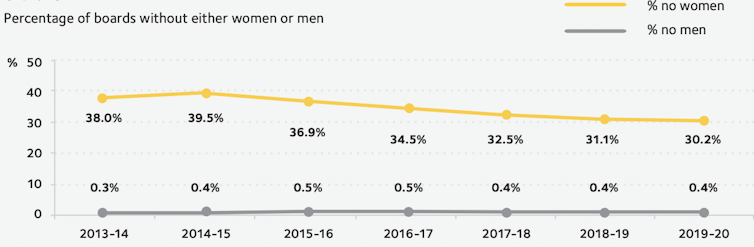
Workplace Gender Equity Agency data[5] paint a grim picture. Women hold only 14.6% of chair positions and 28.1% of directorships in Australia. A mere 18.3% of CEOs and 32.5% of key management personnel are women. Gender equity in leadership roles has even gone backwards[6] in recent years.
Nearly a third of boards and governing bodies[7] have no female directors. By contrast, less than 1% of boards[8] have no male directors.
















