Why most economists continue to back lockdowns
- Written by John Quiggin, Professor, School of Economics, The University of Queensland
With the prospect of a lengthier lockdown looming over Sydney, the idea of “living with the virus” has resurfaced[1].
NSW’s health minister, Brad Hazzard, raised the prospect of abandoning the lockdown and accepting that “the virus has a life which will continue in the community” at a press conference on Wednesday[2]. NSW Premier Gladys Berejiklian and Prime Minister Scott Morrison have rejected that idea, but many voices in the media have been pushing it.
As with pandemic policy in general, much of the discussion of the Sydney outbreak has framed the problem as one pitting health against the economy[3]. In this framing, epidemiologists and public health experts are seen as the advocates of saving lives, while economists are seen as the advocates of saving money.
Read more: Open letter from 265 Australian economists: don't sacrifice health for 'the economy'[4]
In reality, the great majority[5] of Australian economists support policies of aggressive suppression or elimination — that is, keeping case numbers close to zero, and clamping down when an outbreak threatens.
Broad agreement
As with epidemiologists, that broad agreement encompasses a range of views about the appropriate response in any particular case.
Some economists, and some epidemiologists, supported the NSW government’s decision to delay a lockdown, while others wanted earlier action. But only a minority in either group support the idea of ending restrictions and waiting for herd immunity to protect us.
Unfortunately, as we have already seen in the case of climate change, many media outlets thrive on conflict. It is more interesting to present a debate between a pro-lockdown public health expert and an anti-lockdown economist than to present a nuanced discussion of the best way to suppress the virus, taking into account insights from a range of disciplines.
Understanding exponential growth
Why have economists endorsed the policy of suppression with more enthusiasm than, for example, political and business leaders?
First, because economists understand the concept of exponential growth.
While economics’ stress on growth is rightly contested, its centrality to economic concepts means related concepts from epidemiology, such as the reproduction number (R), are immediately comprehensible to us.
Once you understand how rapidly exponential processes can grow, the idea that lockdowns are “disproportionate responses to a handful of cases”, as The Australian has editorialised[6], loses its superficial attraction.
A clear majority of economists surveyed by The Conversation in May 2020[7] (after the end of the national lockdown) supported strong social distancing measures to keep R below 1. Most of those who disagreed felt alternative measures could hold R below 1 at lower costs. Only a handful supported a “let it rip” strategy.
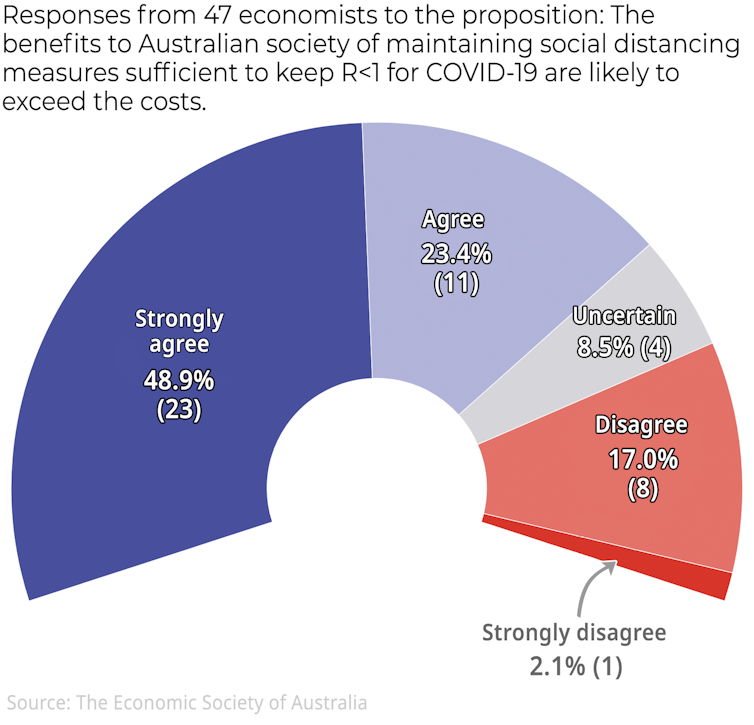 The Conversation, CC BY-ND[8]
Read more:
Economists back social distancing 34-9 in new Economic Society-Conversation survey[9]
Considering counterfactuals
Second, economists understand counterfactuals — that is, the need to specify what would have happened under an alternative policy.
It is easy to make the point that lockdowns are both economically costly and psychologically traumatic. But the counterfactual is not a situation where the economy is unaffected and everyone is happy. Living in fear of the virus, and watching family and friends suffer and die from it, is psychologically traumatic.
As regards the economic costs, the steps people take to reduce their exposure to risk are themselves costly, as is the need to allocate medical resources to treat the sick.
Read more:
Yes, lockdowns are costly. But the alternatives are worse[10]
Weighing trade-offs
Third, and most importantly, economists understand about trade-offs.
There are always trade-offs within the space of policy choices. Should we lock down at the first sign of an outbreak and risk unnecessary costs, or wait until later and risk a longer and harsher lockdown? Should we incur the costs of purpose-built quarantine facilities, or accept the greater risk of leakage from hotel quarantine?
Economists also understand that not all choices involve trade-offs. Sometimes one policy is unequivocally worse than another, on all relevant criteria. While there are always trade-offs somewhere in policy space, it’s often the case that, of the live options, one dominates the other in all important dimensions.
Read more:
Vital Signs: the cost of lockdowns is nowhere near as big as we have been told[11]
On the central question of suppression versus herd immunity, there was no trade-off, as countries like Sweden found out.
The evidence points strongly to one conclusion. Allowing the virus to spread uncontrolled would have done more economic damage than temporary lockdowns, as well as causing thousands of avoidable deaths and tens of thousands to suffer severe, and possibly long-lasting, illness.
Risk and uncertainty
Finally, economists understand the complexities of risk and uncertainty.
One implication is the benefit of diversification by “backing every horse in the race”, as opposed to “putting all your eggs in one basket”, or even a few.
The federal government’s vaccine policy relied heavily on a limited range of options — primarily AstraZeneca, and the University of Queensland’s vaccine venture — both of which ran into problems. If we had followed the logic of diversification, we would be much better placed than we are now.
Economics doesn’t have all the answers. No one knows that better than economists. Dealing with the pandemic requires insights from a range of disciplines. But lazy stereotypes, pitting one profession against another, don’t help.
The Conversation, CC BY-ND[8]
Read more:
Economists back social distancing 34-9 in new Economic Society-Conversation survey[9]
Considering counterfactuals
Second, economists understand counterfactuals — that is, the need to specify what would have happened under an alternative policy.
It is easy to make the point that lockdowns are both economically costly and psychologically traumatic. But the counterfactual is not a situation where the economy is unaffected and everyone is happy. Living in fear of the virus, and watching family and friends suffer and die from it, is psychologically traumatic.
As regards the economic costs, the steps people take to reduce their exposure to risk are themselves costly, as is the need to allocate medical resources to treat the sick.
Read more:
Yes, lockdowns are costly. But the alternatives are worse[10]
Weighing trade-offs
Third, and most importantly, economists understand about trade-offs.
There are always trade-offs within the space of policy choices. Should we lock down at the first sign of an outbreak and risk unnecessary costs, or wait until later and risk a longer and harsher lockdown? Should we incur the costs of purpose-built quarantine facilities, or accept the greater risk of leakage from hotel quarantine?
Economists also understand that not all choices involve trade-offs. Sometimes one policy is unequivocally worse than another, on all relevant criteria. While there are always trade-offs somewhere in policy space, it’s often the case that, of the live options, one dominates the other in all important dimensions.
Read more:
Vital Signs: the cost of lockdowns is nowhere near as big as we have been told[11]
On the central question of suppression versus herd immunity, there was no trade-off, as countries like Sweden found out.
The evidence points strongly to one conclusion. Allowing the virus to spread uncontrolled would have done more economic damage than temporary lockdowns, as well as causing thousands of avoidable deaths and tens of thousands to suffer severe, and possibly long-lasting, illness.
Risk and uncertainty
Finally, economists understand the complexities of risk and uncertainty.
One implication is the benefit of diversification by “backing every horse in the race”, as opposed to “putting all your eggs in one basket”, or even a few.
The federal government’s vaccine policy relied heavily on a limited range of options — primarily AstraZeneca, and the University of Queensland’s vaccine venture — both of which ran into problems. If we had followed the logic of diversification, we would be much better placed than we are now.
Economics doesn’t have all the answers. No one knows that better than economists. Dealing with the pandemic requires insights from a range of disciplines. But lazy stereotypes, pitting one profession against another, don’t help.
References
- ^ has resurfaced (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ on Wednesday (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ health against the economy (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ Open letter from 265 Australian economists: don't sacrifice health for 'the economy' (theconversation.com)
- ^ the great majority (covid19openletter.net)
- ^ has editorialised (www.theaustralian.com.au)
- ^ The Conversation in May 2020 (theconversation.com)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Economists back social distancing 34-9 in new Economic Society-Conversation survey (theconversation.com)
- ^ Yes, lockdowns are costly. But the alternatives are worse (theconversation.com)
- ^ Vital Signs: the cost of lockdowns is nowhere near as big as we have been told (theconversation.com)
Authors: John Quiggin, Professor, School of Economics, The University of Queensland
Read more https://theconversation.com/why-most-economists-continue-to-back-lockdowns-164239