We found a new type of stellar explosion that could explain a 13-billion-year-old mystery of the Milky Way's elements
- Written by David Yong, Academic, Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Australian National University
Until recently it was thought neutron star mergers were the only way heavy elements[1] (heavier than Zinc) could be produced. These mergers involve the mashup of the remnants of two massive stars in a binary system.
But we know heavy elements were first produced not long after the Big Bang, when the universe was really young. Back then, not enough time had passed for neutron star mergers to have even occurred. Thus, another source was needed to explain the presence of early heavy elements in the Milky Way.
The discovery of an ancient star SMSS J2003-1142 in the Milky Way’s halo — which is the roughly spherical region that surrounds the galaxy — is providing the first evidence for another source for heavy elements, including uranium and possibly gold.
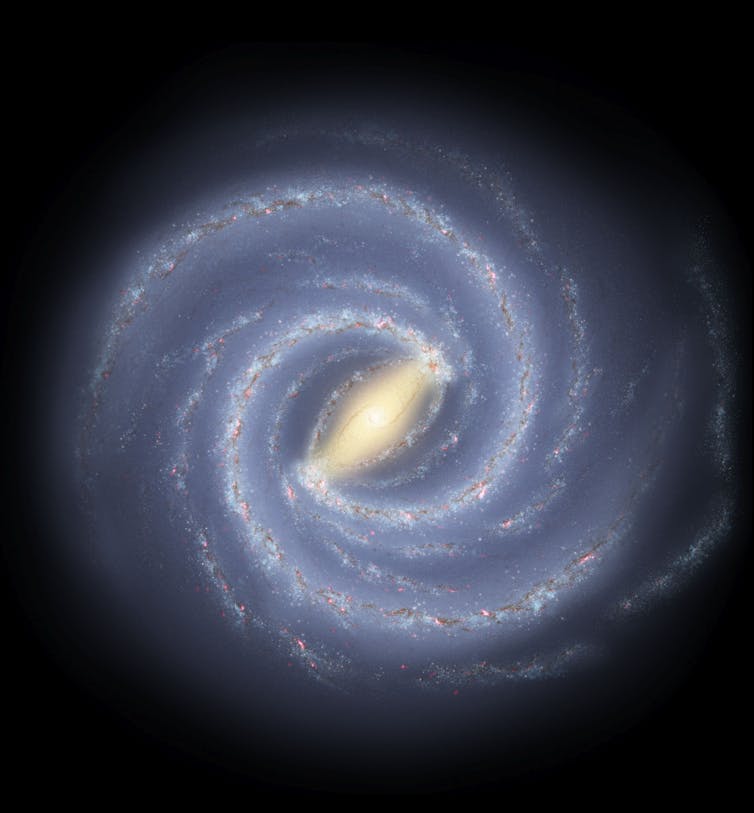 Around our galaxy, the Milky Way, there is a ‘halo’ made up of hot gases which is continually being supplied with material ejected by birthing or dying stars. Only 1% of stars in the galaxy are found in the halo.
NASA
Around our galaxy, the Milky Way, there is a ‘halo’ made up of hot gases which is continually being supplied with material ejected by birthing or dying stars. Only 1% of stars in the galaxy are found in the halo.
NASA
In our research published today[2] in Nature, we show the heavy elements detected in SMSS J2003-1142 were likely produced, not by a neutron star merger, but through the collapse and explosion of a rapidly spinning star with a strong magnetic field and a mass about 25 times that of the Sun.
We call this explosion event a “magnetorotational hypernova”.
Stellar alchemy
It was recently confirmed[3] that neutron star mergers are indeed one source of the heavy elements in our galaxy. As the name suggests, this is when two neutron stars in a binary system merge together in an energetic event called a “kilonova”. This process produces heavy elements.
 Binary star systems have two stars orbiting around a common centre of mass. A neutron star merger is a type of stellar collision that happens between two neutron stars in a binary system. This process can produce heavy elements.
NASA
Binary star systems have two stars orbiting around a common centre of mass. A neutron star merger is a type of stellar collision that happens between two neutron stars in a binary system. This process can produce heavy elements.
NASA
However, existing models of the chemical evolution of our galaxy indicate that neutron star mergers alone could not have produced the specific patterns of elements we see in multiple ancient stars, including SMSS J2003-1142.
Read more: Signals from a spectacular neutron star merger that made gravitational waves are slowly fading away[4]
A relic from the early universe
SMSS J2003-1142 was first observed in 2016 from Australia, and then again in September 2019 using a telescope at the European Southern Observatory in Chile.
From these observations, we studied the star’s chemical composition. Our analysis revealed an iron content roughly 3,000 times lower than the Sun’s. In other words, SMSS J2003-1142 is chemically primitive.
The elements we observed in it were likely produced by a single parent star, just after the Big Bang.
Signatures of a collapsed rapidly spinning star
The chemical composition of SMSS J2003-1142 can reveal the nature and properties of its parent star. Particularly important are its unusually high amounts of nitrogen, zinc and heavy elements including europium and uranium.
The high nitrogen levels in SMSS J2003-1142 indicate the parent star had rapid rotation, while high zinc levels indicate the energy of the explosion was about ten times that of a “normal” supernova — which means it would have been a hypernova. Also, large amounts of uranium would have required the presence of lots of neutrons.
The heavy elements we can observe in SMSS J2003-1142 today are all evidence that this star was produced as a result of an early magnetorotational hypernova explosion.
And our work has therefore provided the first evidence that magnetorotational hypernova events are a source of heavy elements in our galaxy (alongside neutron star mergers).
What about neutron star mergers?
But how do we know it wasn’t just neutron star mergers that led to the particular elements we find in SMSS J2003-1142? There’s a few reasons for this.
In our hypothesis, a single parent star would have made all the elements observed in SMSS J2003-1142. On the other hand, it would have taken much, much longer for the same elements to have been made only through neutron star mergers. But this time wouldn’t have even existed this early in the galaxy’s formation when these elements were made.
Also, neutron star mergers make only heavy elements, so additional sources such as regular supernova would had to have occurred to explain other heavy elements, such as calcium, observed in SMSS J2003-1142. This scenario, while possible, is more complicated and therefore less likely.
The magnetorotational hypernovae model not only provides a better fit to the data, it can also explain the composition of SMSS J2003-1142 through a single event. It could be neutron star mergers, together with magnetorotational supernovae, could in unison explain how all the heavy elements in the Milky Way were created.
Read more: The race to find even more new elements to add to the periodic table[5]
References
- ^ heavy elements (pls.llnl.gov)
- ^ published today (dx.doi.org)
- ^ confirmed (www.space.com)
- ^ Signals from a spectacular neutron star merger that made gravitational waves are slowly fading away (theconversation.com)
- ^ The race to find even more new elements to add to the periodic table (theconversation.com)

















