Why governments will have to consider the costs of long COVID when easing pandemic restrictions
- Written by Richard Meade, Research Fellow in Economics, and in Social Sciences & Public Policy, Auckland University of Technology
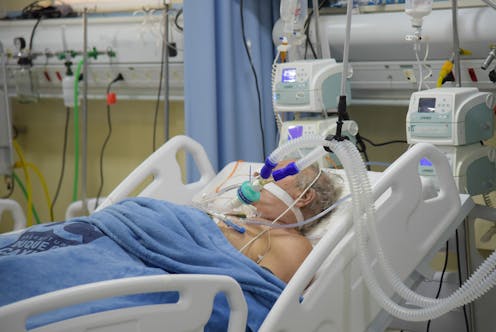
With governments worldwide under pressure to ease pandemic restrictions as vaccination rates rise and impatience with border restrictions grows, new threats become clearer.
One of the costliest, it is now feared, could be a tsunami of “long COVID” cases.
Long COVID is a serious ongoing illness that follows an acute episode of the disease. It is characterised by extreme fatigue, muscle weakness, post-exertional malaise and an inability to concentrate (“brain fog”), among many other symptoms[1].
The focus, therefore, needs to shift towards protecting quality of life as much as saving lives in the first place.
In the UK it is reported[2] two million people have experienced long COVID. Around 385,000 having suffered symptoms for a year or more.
The nation’s so-called “Freedom Day” on July 19 went ahead despite expert warnings of soaring infections, especially among younger and unvaccinated people. A further 500,000 long COVID cases[3] have been predicted during the current wave of infection.
These numbers far outstrip the already staggering 150,000 deaths attributed to the virus[4] in the UK — and the associated costs will be significant.
Putting a price on long COVID
The social costs of long COVID should not be underestimated. For example, suppose an elderly person contracts COVID-19 and dies, when they might otherwise have lived in full health another five years. A health economist would say their early death has cost society five “quality-adjusted life years” (QALYs).
This is usually expressed as a monetary amount that can then be weighed against the cost of saving that person’s life when deciding on appropriate pandemic protections.
Contrast this with a young person contracting COVID-19 and not dying, but suffering long COVID for 10 years, with their estimated quality of life effectively halved while unwell.
Read more: Long COVID: with one in three patients back in hospital after three months, where are the treatments?[5]
They too will have lost an estimated five QALYs — the same social cost as the elderly person who died.
This means if we ease pandemic restrictions on the basis that people are no longer dying, we might be facing equally serious social costs from long COVID.
If long COVID is chronic and much more common than death from COVID (as the current data strongly suggest), the costs rise further. If sufferers of long COVID also face shortened lives, having endured years of debilitation and misery, the costs rise again.
Rough first estimates[6] suggest the overall economic cost of long COVID could be almost half the cost of COVID-related deaths in the UK.
For younger people, however, the social costs of long COVID are estimated to far outstrip those of dying, meaning they will carry a disproportionate burden of the pandemic’s long-term costs.
Comparison with chronic fatigue syndrome
Long COVID is often likened to chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), which is sometimes called ME (for myalgic encephalomyelitis). Both are characterised as a form of “post-viral fatigue syndrome”, with CFS leaving sufferers seriously debilitated[7] and unable to maintain normal lives — often for years, even decades.
While we have no long-term data to gauge how chronic or serious long COVID might be, we should be mindful that it could be as long-lived as CFS.
Furthermore, long COVID is also reported[8] to affect multiple organs in measurable ways, including damage to major organs like the heart and lungs.
Consequently, long COVID could shorten lives, if not end them. This distinguishes it from CFS which – frustratingly, for sufferers wanting to be taken seriously – lacks recognised objective markers.
Read more: The mystery of 'long COVID': up to 1 in 3 people who catch the virus suffer for months. Here's what we know so far[9]
Protecting quality of life
On a personal note, I suffered CFS for 11 years and recovered in 2004. It emerged after a flu-like illness in 1993, which evolved into a constellation of symptoms that defied explanation or treatment.
Recovery required years off work and, with the care and support of family and friends, patient and determined rebuilding of my ability to lead a normal life.
The condition involved huge personal, social and professional costs. I was unable to maintain a normal life, relationships and work commitments. Constant ill health, with no end in sight, was enormously frustrating and miserable.
Read more: I went from regular TV commentator on COVID to long COVID sufferer in just a few months[10]
It never helped that medical practitioners were either incredulous or believed I was unwell but had no real solutions to offer.
Like CFS, long COVID is a serious condition that cannot be taken lightly. Even if not fatal, it can still seriously affect the sufferer’s quality of life. Hence, policymakers need to consider the social costs of long COVID when deciding when and how to ease pandemic restrictions.
Our pandemic response will need to be as much about protecting quality of life as it has been about saving lives. We need to take serious steps to keep long COVID at bay.
References
- ^ many other symptoms (www.sciencealert.com)
- ^ reported (www.independent.co.uk)
- ^ 500,000 long COVID cases (www.independent.co.uk)
- ^ 150,000 deaths attributed to the virus (coronavirus.data.gov.uk)
- ^ Long COVID: with one in three patients back in hospital after three months, where are the treatments? (theconversation.com)
- ^ first estimates (www.nature.com)
- ^ seriously debilitated (www.cdc.gov)
- ^ reported (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ The mystery of 'long COVID': up to 1 in 3 people who catch the virus suffer for months. Here's what we know so far (theconversation.com)
- ^ I went from regular TV commentator on COVID to long COVID sufferer in just a few months (theconversation.com)

















