climate change is making workers' lives more difficult
- Written by Lauren Rickards, Professor, RMIT University
“Work” – broadly defined – is what allows society to function. Like other old certainties, it is under threat from climate change.
A key reason climate-related stresses and disruptions can have such a big impact is precisely because of their effect on the work we do and on the wider system of work we rely on. But little attention has been given to the urgent need to adapt work to climate change.
Our new report on climate impacts at work[1], released today, documents emerging serious risks.
A female professional told us: “there were days where I simply had to use up sick leave because it was too hot to get safely to work”.
One male sales worker told us about working during the Black Summer of 2019/2020:
Smoke from bushfires two years ago was intolerable. The heat also was horrific at times. During the smokiest days temperatures often shot up to over 40 degrees. It was like the planet Venus. My employer … provided no masks at all at that time, despite numerous requests, even pleadings.
Australia is already 1.4℃ warmer[2] than it was in 1910. Climatic extremes and events like the 2022 floods and Black Summer – as well as many less visible disruptions – are already undermining our capacity to work across different organisations, industries and sectors.
We will have to get better at adapting to our changed climate – and quickly.
We found the effects of climate change on workers reach more widely than than previously thought.
In short, no one is immune to climate harms, whether indoor or outdoor, junior or senior. Given we rely on each others’ work, that means climate change impacts are likely to increasingly “cascade” through society, as the 2022 IPCC report on Australasia[3] details.
Our research comes from a survey of 1,165 workers across ten industries undertaken in the first half of 2022, assisted by six unions. The sample is not representative of the workforce as a whole and is skewed towards types of workers not typically considered on harms from climate change, such as professionals and community and personal service workers.
Read more: Unions can – and will – play a leading role in tackling the climate crisis[4]
Previous research has documented the serious ways heat affects workers[5], especially those outdoors or in poorly cooled spaces. Other studies[6] have found outdoor council workers and delivery cyclists in Sydney are already having to use coping mechanisms such as extra breaks, lighter duties and temporarily stopping work to try to avoid heat stress.
Our data similarly points to heat’s health impacts. Outdoor workers were especially likely to report being tired and fatigued, dehydrated and less productive. They were also more likely to sweat excessively and be sunburnt.
Less recognised is that indoor workers are also being affected by heat and smoke.
These health impacts are serious. Close to 450 people died from the effects of smoke inhalation over the Black Summer[7]. These issues were compounded by the COVID pandemic, notably for those workers who have to had to wear personal protective equipment or work from poorly cooled houses during heatwave conditions.
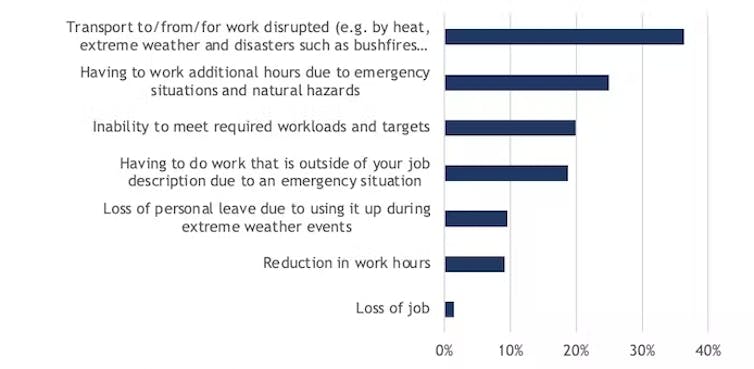
Climate change can undermine people’s capacity to work in other ways. Some workers reported impacts on the amount and focus of their work. For example, some had to take on new tasks to cover for colleagues who were overwhelmed or furloughed due to the Black Summer fires. A quarter reported having to work additional hours due to emergency situations such as the floods, while others reported they had lost hours, had to take personal leave or even lost their job as a result of climatic events.
There are even impacts from climatic effects on the wider public. Half of the survey respondents reported having to manage angrier customers, while 60% said climatic events had led to staffing disruptions. Some reported extreme weather was causing supply chain disruption.
One male professional said:
The frequency of storm events has noticeably increased, and these storms are often more severe with higher wind speeds and rates of precipitation than in the past. […] Our workload has increased accordingly and risk to people and property has also increased.
Management are struggling to come to terms with the frequency and severity of storm events and this is leading to anxiety and conflict with management in relation to the perceived need to close the site, or part of it, during severe weather events. Site closure protects individuals from harm […] but is bad for revenue raising for the many businesses that operate on our site.
Our capacity to work often relies on intricate systems of settlements, infrastructure and services that consist of workplaces and support others. When any of these workplaces are affected, there are flow-on effects.
Our survey found more than a third of workers had not been able to travel to work due to climatic factors. If trains don’t run or roads are blocked, it can bring many workplaces to a halt.
We are now enmeshed in a different climate to the one we grew up in – and it will change more.
To make our societies and systems resilient to climate change, we will have to adapt how, where, when we work, who “we” is, what we work on, and why. This adaptation work is urgent. No one is immune.
Read more: As heatwaves become more extreme, which jobs are riskiest?[8]
References
- ^ climate impacts at work (cur.org.au)
- ^ already 1.4℃ warmer (www.science.org.au)
- ^ 2022 IPCC report on Australasia (www.ipcc.ch)
- ^ Unions can – and will – play a leading role in tackling the climate crisis (theconversation.com)
- ^ heat affects workers (unitedworkers.org.au)
- ^ studies (www.uts.edu.au)
- ^ Black Summer (theconversation.com)
- ^ As heatwaves become more extreme, which jobs are riskiest? (theconversation.com)

















